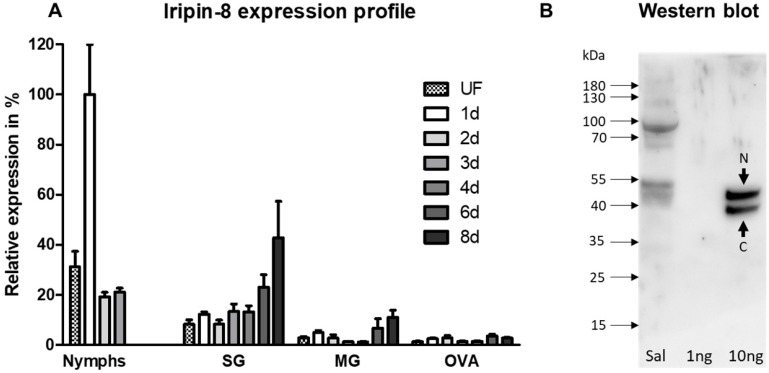
Figure 1.
Iripin-8 expression in ticks and its presence in tick saliva. (A) Pools of I. ricinus salivary glands, midguts, and ovaries from female ticks and whole bodies from nymphs were dissected under RNase-free conditions. cDNA was subsequently prepared as a template for qRT-PCR. Iripin-8 expression was normalized to elongation factor 1α and compared between all values with the highest expression set to 100% (y-axis). The data show an average of three biological replicates for adult ticks and six replicates for nymphs (±SEM). SG = salivary glands; MG = midguts; OVA = ovaries; UF = unfed ticks; 1 d, 2 d, 3 d, 4 d, 6 d, 8 d = ticks after 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, or 8 days of feeding. For nymphs, the last column represents fully fed nymphs. All feeding points for each development stage/tissue are compared with the unfed ticks of the respective group. (B) Iripin-8 can be detected in tick saliva by Western blotting. Saliva from ticks after 6 days of feeding and recombinant Iripin-8 protein were visualized by Western blotting using serum from naïve and Iripin-8-immunized rabbits. Sal = tick saliva; 1 ng, 10 ng = Iripin-8 recombinant protein at 1 ng and 10 ng load. N: native Iripin-8, C: cleaved Iripin-8.