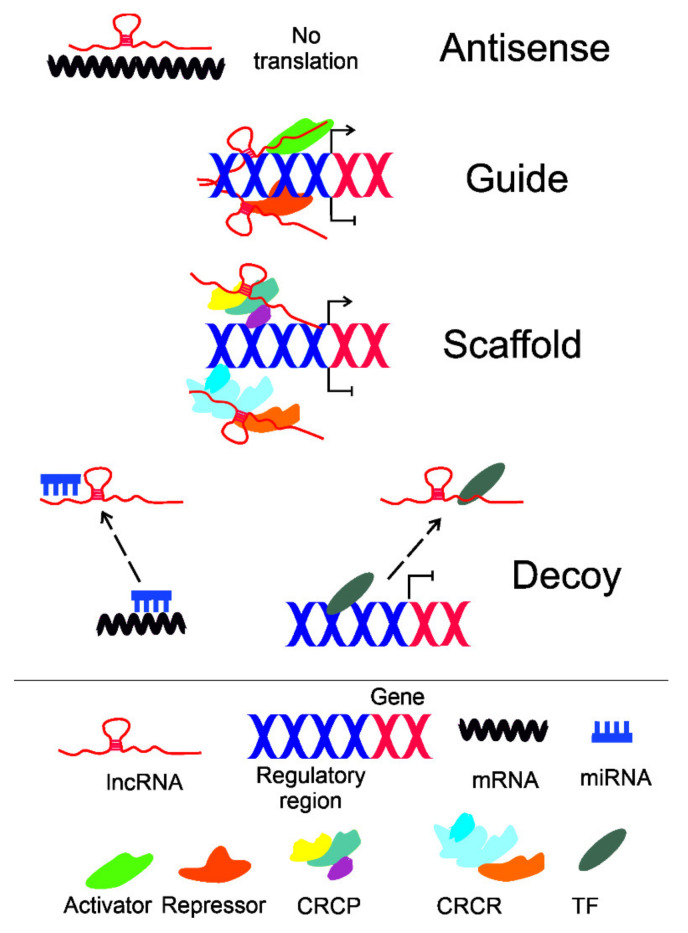
Figure 3.
Basic modes of the cellular action of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in the regulation of gene expression: antisense, guide, scaffold, and decoy. A lncRNA may pair with a complementary fragment of mRNA, preventing or inhibiting its translation. A lncRNA recruits and/or guides transcriptional activators and repressors to activate/repress transcription of the target gene. A lncRNA may serve as a platform (scaffold) to facilitate assembling a chromatin remodeling complex to change the structure of chromatin into a more open (CRCP—chromatin remodeling complex acting permissively) or closed (CRCR—chromatin remodeling complex acting repressively) configuration. A lncRNA may act as a decoy to recruit (broken arrows) micro RNAs (miRNAs) or transcriptional factors (TFs) and sequester them from their target mRNA or DNA, respectively. Presented are only examples of lncRNAs actions in gene expression regulation, and many other mechanisms, e.g., those related to translation and post-translational regulations, are not illustrated, but in general, they follow the presented schemes. Some modes of action of lncRNAs may overlap.