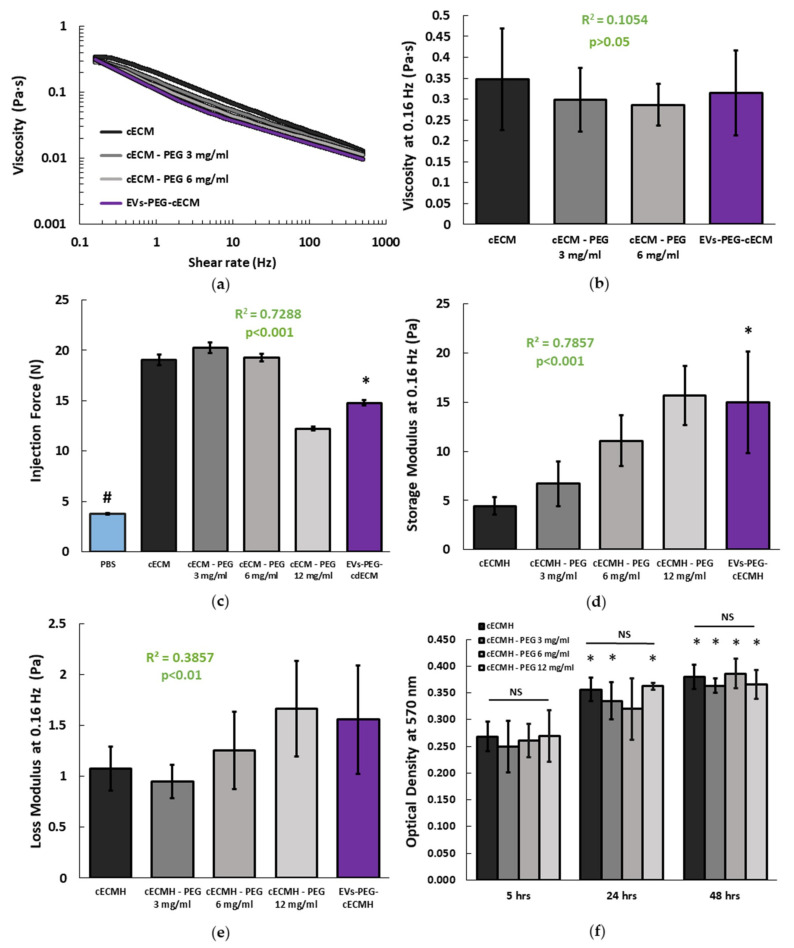
Figure 3.
Mechanical properties and degradation of the cECMH alone, with PEG, and with PEG-isolated EVs. (a) Average viscosity of the different hydrogel solution formulations (n = 3 for each condition, each in triplicate). (b) Viscosity at 0.16 Hz (n = 3). Squared Pearson’s correlation coefficient for PEG concentration in the cECMH vs. viscosity at 0.16 Hz and its significance (p > 0.05). (c) Force required for injection (n = 3). Squared Pearson’s correlation coefficient for PEG concentration in the cECMH vs. injection force and its significance (p < 0.001). * p < 0.001 vs. cECMH. # p < 0.001 vs. all other groups. (d) Storage modulus at 0.16 Hz (n = 4). Squared Pearson’s correlation coefficient for PEG concentration in the cECMH vs. storage modulus and its significance (p < 0.001). * p < 0.01 vs. cECMH. (e) Loss modulus at 0.16 Hz (n = 4). Squared Pearson’s correlation coefficient for PEG concentration in the cECMH vs. loss modulus and its significance (p < 0.01) (f) Enzymatic degradation (soluble amines, n = 6, each in triplicate). * p < 0.05 with respect to their same group at 5 h. cECMH, cardiac extracellular matrix hydrogel; PEG, polyethylene glycol; EVs, extracellular vesicles.