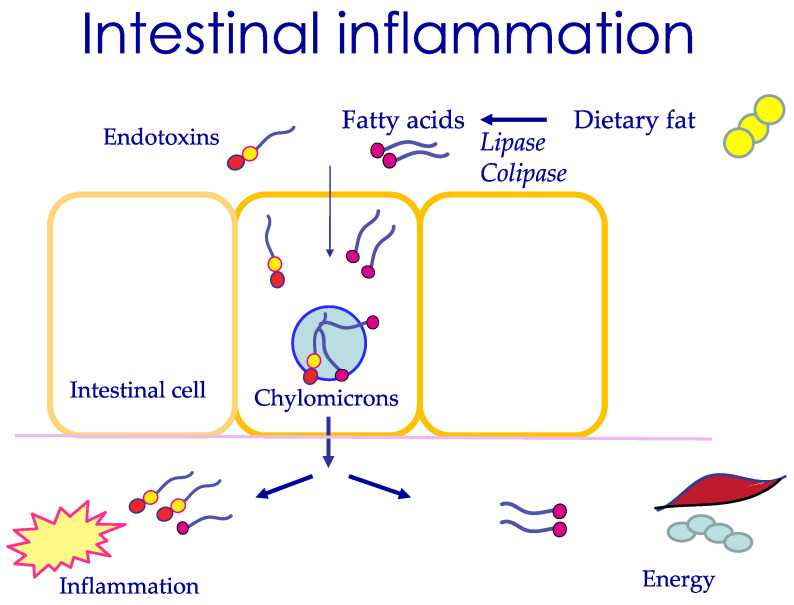
Figure 1.
Intestinal uptake of endotoxins occurs with uptake of dietary fat after this has been hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase and its protein cofactor lipase to fatty acids. In the intestinal cell, chylomicrons are formed and leave through passage into the lymph. Endotoxins have the potential to induce inflammation. Fatty acids are primarily used as an energy source but may also induce inflammation.