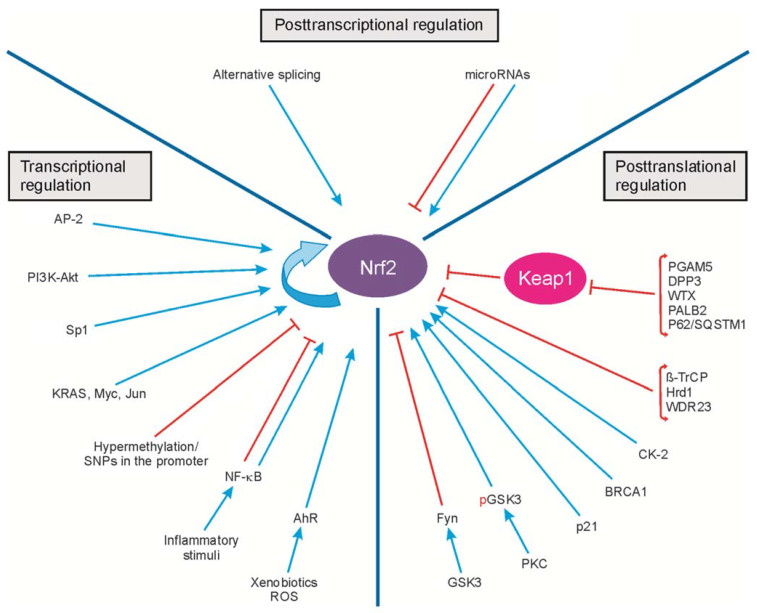
Figure 2.
Transcriptional, posttranscriptional and posttranslational regulation of Nrf2 activity. The transcription of Nr2 is regulated by the transcription factors, oncogenes (KRAS, Myc, Jun) and modifications of the Nrf2 promoter (hypermethylation or SNPs). Posttranscriptional regulation includes alternative splicing and microRNA binding. The posttranslational control of Nrf2 activity results from protein modifications, protein degradation and protein–protein interactions. Arrows and blunt ends indicate activation and inhibition, respectively. ROS, reactive oxygen species; SNPs, single nucleotide polymorphisms; Akt, serine/threonine-protein kinase; BRCA1, breast cancer susceptibility 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Fyn, tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn; GSK-3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; pGSK-3, phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase-3; KRAS, GTPase KRas; Myc, Myc proto-oncogene protein; Jun, transcription factor AP-1; AP-2, activating enhancer-binding protein 2; Sp1, specificity protein 1; PKC, protein kinase C; CK-2, casein kinase 2; β-TrCP, β-transducin repeat-containing protein; Hrd1, HMG-CoA reductase degradation 1; WDR23, WD-repeat protein 23; PGAM5, phosphoglycerate mutase 5; DPP3, dipeptidyl peptidase 3; WTX, Wilms tumor gene on the X chromosome; PALB2, partner and localizer of BRCA2; p21, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1; p62/SQSTM1, sequestosome 1. Figure adapted from [67].