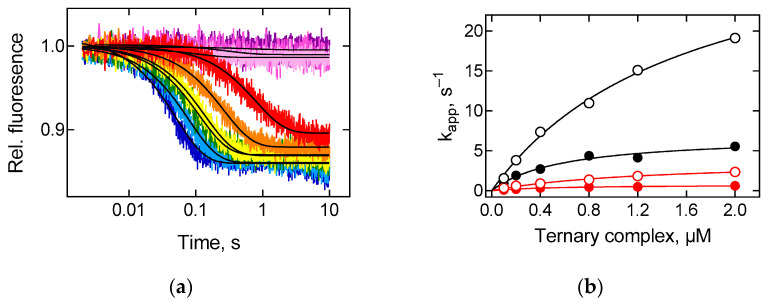
Figure 1.
A-site binding kinetics. The ribosomal complexes containing Prf-labelled fMet-tRNAMet in the P site were rapidly mixed with an increasing amount of ternary complex, EF-Tu∙GTP∙Phe-tRNAPhe. (a) Fluorescence time courses of Prf-labelled ribosomal complex (0.05 µM) interaction with ternary complex (0.1 μM, red; 0.2 μM, orange; 0.4 μM, yellow; 0.8 μM, green; 1.2 μM, blue; 2 μM, dark blue), containing EF-Tu from E. coli at 37 °C. The reaction in the presence of inhibitors of A-site binding kirromycin (150 µM, light pink), tetracycline (30 µM, pink) or with buffer TAKM7 (violet). Each time course reflects the average of 5–7 technical replicates. Black lines show single-exponential fits. (b) Concentration dependence of apparent rate constants (kapp) on ternary complex (0.1–2 μM). kapp values were estimated by the single-exponential fitting of time courses as (a) for A-site reactions with EF-Tu from E. coli at 20 °C (black circles), at 37 °C (black open circles), EF-Tu from T. thermophilus at 20 °C (red circles), at 37 °C (red open circles). Lines show hyperbolic fits, and numerical values are provided in the text. Error bars (s.e.m.) are calculated by the GraphPad Prism software from 5 to 7 technical replicates for each concentration; however, they do not exceed the size of symbols.