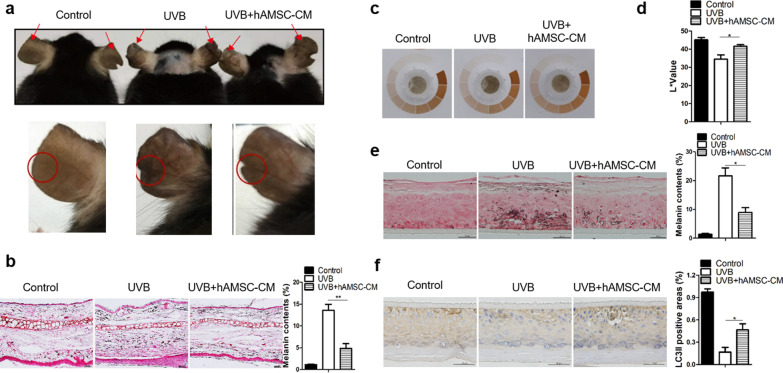
Fig. 4.
hAMSC-CM inhibited the UVB-induced melanin productions by modulating autophagy in vivo. a C57BL/6 mice were irradiated with UVB at a dose of 150 mJ/cm2 for 14 days. hAMSC-CM was injected into the lower edge of ears at the eighth day. Arrows indicate pigmentation differences of ear skin with or without hAMSC-CM treatment. Epidermis of ear skin containing melanocytes was different from trunk/fur-bearing skin, and more suitable for research. b Ear slices from the mice shown in a were subjected to Fontana-Masson staining for the analysis of melanin production. Scale bar = 20 μm. The relative areas positive for melanin per whole epidermis were statistically analyzed. c Photograph of 3D-HSSs pre-treated with UVB were incubated with or without hAMSC-CM. d The intensity of pigmentation in 3D-HSSs were measured by a colorimeter on the eighth day and were expressed as the L* values. Values represent the average of three samples (mean ± SD). e Skin tissues from the 3D-HSSs shown in (c) were subjected to Fontana-Masson staining for the analysis of melanin content. Scale bar = 50 μm. The relative areas positive for melanin per whole epidermis were statistically analyzed. f Representative histological images of LC3B expression in skin tissues from the 3D-HSSs shown in c. Scale bar = 50 μm. The relative areas positive for LC3II were statistically analyzed. Data are presented as mean ± SD. The experiments were repeated three times independently and the data of one representative experiment was shown. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001