Fig. 1. Identification of mammalian retroelement derived Gag homologs that form capsids and are secreted.
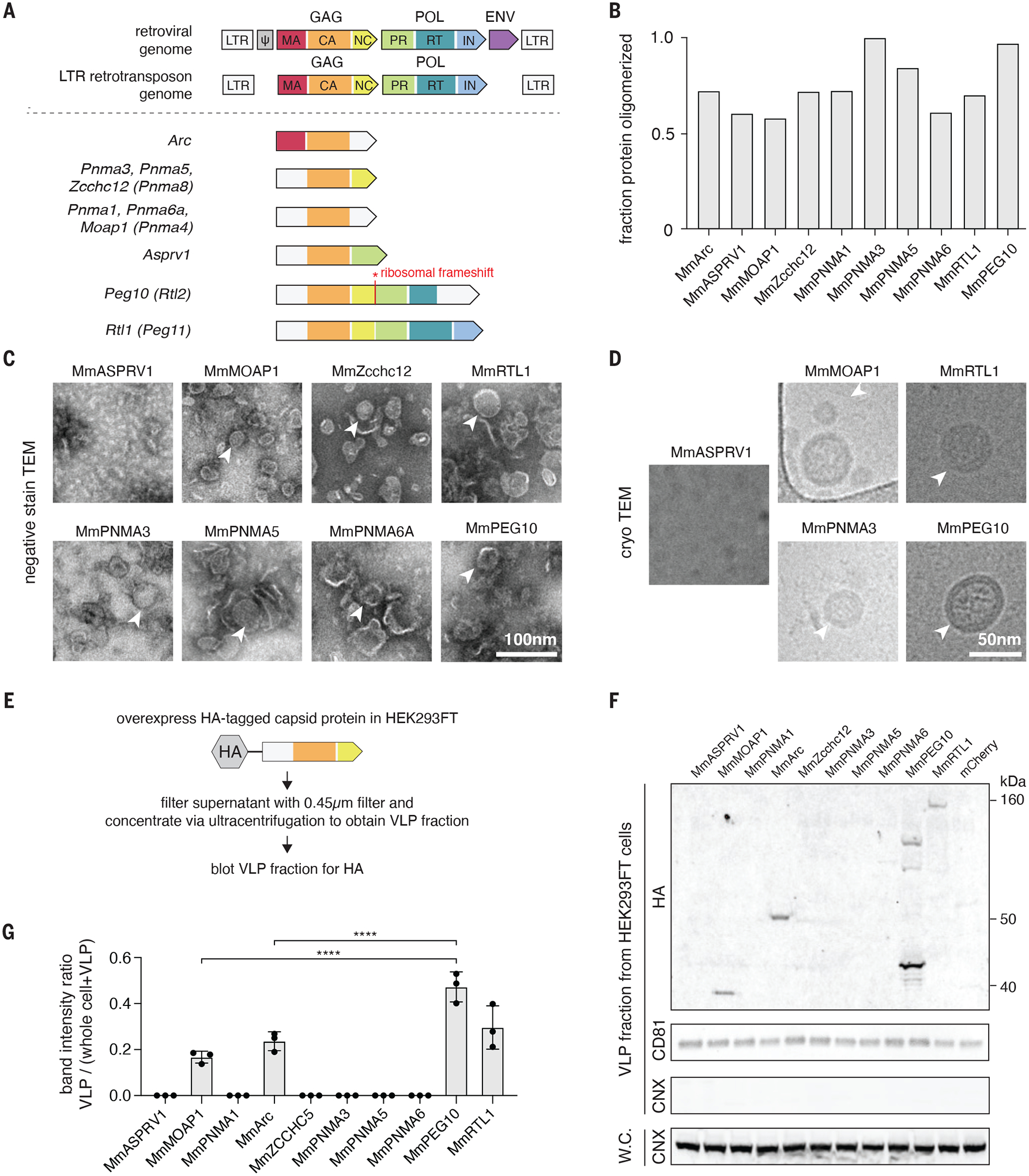
A. Domain architectures of selected Capsid (CA)-containing mammalian Gag homologs compared to that of typical retrovirus and LTR retrotransposons. Each group of Gag homologs contains a distinct combination of predicted CA, Nucleocapsid (NC), Protease (PR), and Reverse Transcriptase (RT) domains. LTR, long terminal repeat; MA, matrix; IN, integrase.
B. Fraction of the total bacterially-produced protein that forms oligomers (>600 kD), as determined by size exclusion chromatography.
C. Representative negative stain transmission electron micrographs (TEM) of the Mus musculus (Mm) orthologues of the CA-domain containing proteins. Scale bar, 100 nm.
D. Representative electron micrographs using cryogenic electron microscopy (cryoTEM) of a selected subset of the identified CA-domain containing proteins. Scale bar, 50 nm.
E. Method for detecting extracellular forms of CA-domain containing homologs.
F. Representative blots of CA-domain containing proteins in the cell-free fraction. CD81 was used as loading control for the ultracentrifuged cell-free fraction. Whole cell (W.C.) and VLP fraction blots for the endoplasmic reticulum marker CALNEXIN (CNX) ensure equal loading of whole cell protein and the purity of cell-free VLP fraction.
G. Quantification of extracellular CA-domain containing proteins (as in F) based on n=3 replicates.
