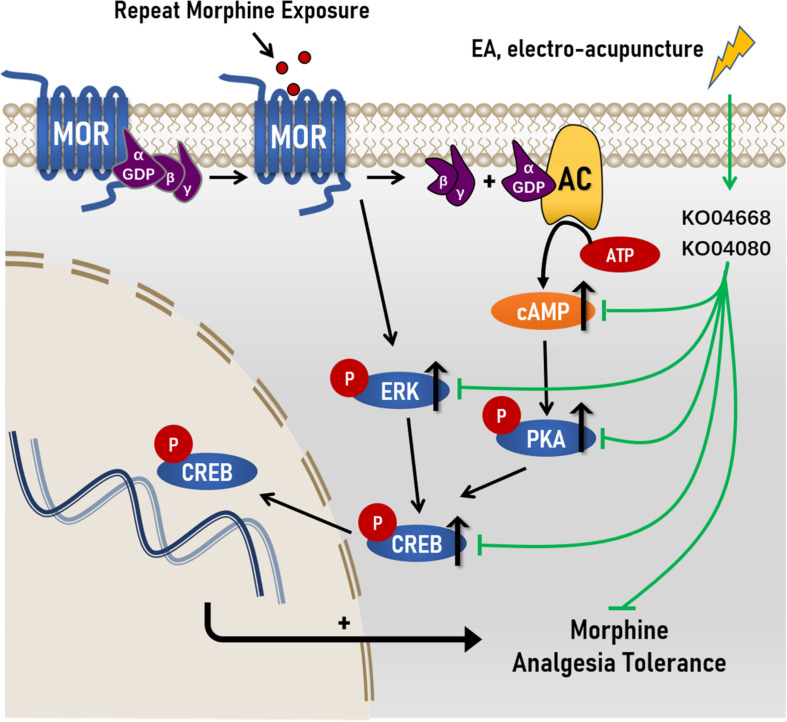
FIGURE 7.
Proposed mechanisms of action by which EA ameliorated morphine-induced tolerance in mice. Chronic morphine increased the levels of cAMP, and the levels of phosphorylation levels of protein kinase A (PKA), extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK) and cAMP response element-binding (CREB) in morphine-induced tolerance. After the treatment of Electro-Acupuncture, the increased of cAMP, p-PKA C, p-ERK, and p-CREB were significantly decreased in morphine-induce tolerance. Simultaneously, RNA sequencing reval the underlying molecular targets of EA treatment on morphine-induced tolerance maybe KO04080 (Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction) and KO04668 (TNF signaling pathway).