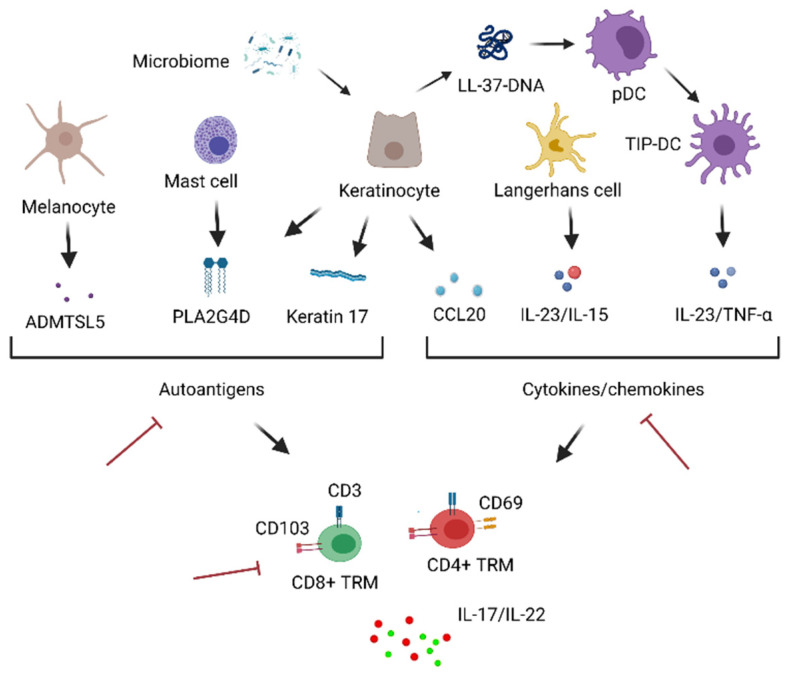
Figure 2.
Development of TRM in psoriasis. TRM are activated by either autoantigens or cytokines/chemokines. Autoantigens include ADMTSL5 on the surface of melanocytes, PLAG4D from mast cells and keratinocytes, and keratin 17 from keratinocytes. Antimicrobial peptide LL-37, also from keratinocytes, binds to self-DNA to activate pDC and TIP-DC, leading to the production of IL-23/TNF-α. IL-23/15 from Langerhans cells and CCL20 from keratinocytes also activate TRM. These stimulated TRM produce proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-17A and IL-22, the hallmarks of psoriasis. The development of pathogenic TRM can be inhibited by stopping pathways related to TRM activation or directly inhibiting the activity of TRM (red inhibition icon). Created with BioRender.com (assessed on 21 August 2021).