FIGURE 2.
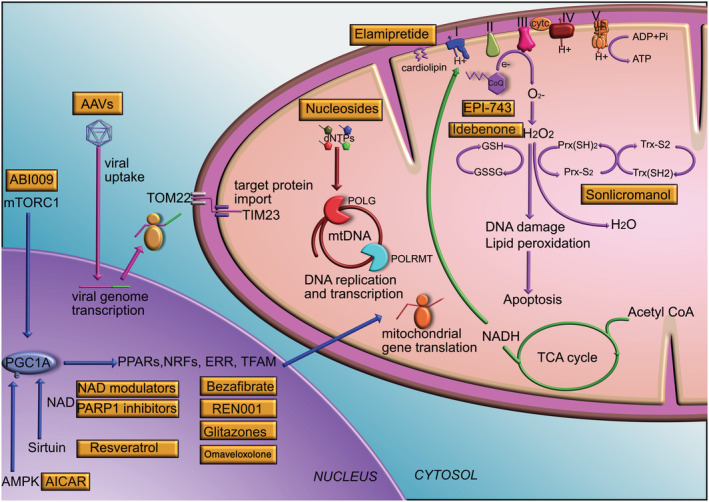
Mechanisms of action of emerging therapies. Drugs affecting mitochondrial biogenesis act on the PGC1α pathway. PGC1α is a master transcriptional coactivator of several transcription factors including PPARα,δ,γ, NRF1,2, ERR and TFAM. PGC1α is activated by phosphorylation by AMPK and deacetylation by NAD+‐dependent sirtuin, and is also controlled by mTOR. Drugs acting on these pathways include AICAR which activates AMPK, resveratrol which activates sirtuin, NAD+ modulators and PARP1 inhibitors which increase NAD+ levels, rapamycin and ABI009 which act on mTORC1, bezafibrate which activates PPARα, REN001 which activates PPARδ, glitazones which activate PPARγ and omaveloxolone which activates NRF2. Gene therapy vectors for example, AAVs transduce target cells by first being endocytosed at the plasma membrane. The viral genome is released in the nucleus where it forms an episome and is transcribed by target cell transcriptional machinery. mRNAs are translated in the cytosol. The nascent protein contains a mitochondrial targeting sequence which enables entry into mitochondria by interacting with the TOM22/TIM23 complex. Nucleoside based trial drugs are currently only applicable to one subtype of MDDS, namely thymidine kinase 2 deficiency. Several candidate therapies act on pathways related to the production of ROS, such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Their intermediates have important cellular signalling functions, but also contribute to disease pathophysiology and cell death in mitochondrial disease. Levels of ROS are controlled by the glutathione and peroxidoredoxin/thioredoxin pathways. EPI743 and idebenone are both CoQ analogues which are thought to affect glutathione levels and Sonlicromanol acts on the peroxidoredoxin/thioredoxin pathway. Key: AAV, adeno‐associated virus; cytc, cytochrome c; CoQ, coenzyme Q; AMPK, AMP activated protein kinase; GSH, glutathione (reduced); GSSG, glutathione (oxidised); ERR, oestrogen related receptor; MDDS, mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome; mRNA, messenger RNA; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NRF, nuclear respiratory factor; PARP1, poly(ADP‐ribose) polymerase 1; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor gamma coactivator 1‐alpha; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor; POLG, polymerase gamma; Prx, peroxiredoxin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TFAM, transcription factor A, mitochondrial; TIM, translocase of inner membrane; TOM, translocase of outer membrane; Trx, thioredoxin
