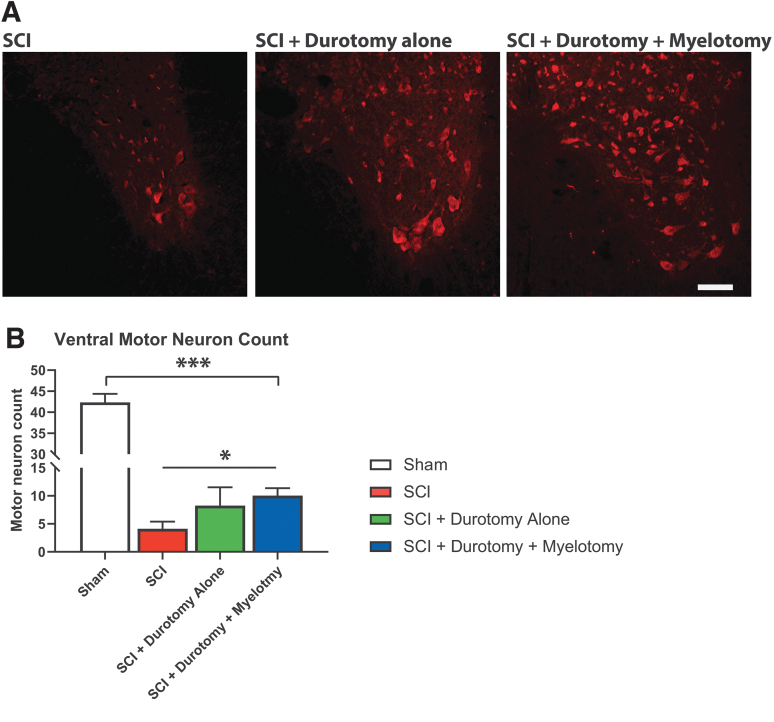
FIG. 3.
Effect of surgical decompression on local motor neurons. (A) Representative examples of NeuN stained axial histological slides. (B) Histological analysis revealed that thoracic contusion spinal cord injury resulted in a significant decrease in ventral horn motor neuron counts at the injury center 8 weeks after injury (p < 0.001). Surgical decompression of the spinal cord, either by durotomy alone or durotomy plus myelotomy led to a trend toward an increase in the number of spared ventral horn motor neurons, although this was only significant following durotomy plus myelotomy (p < 0.05). ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. Color image is available online.