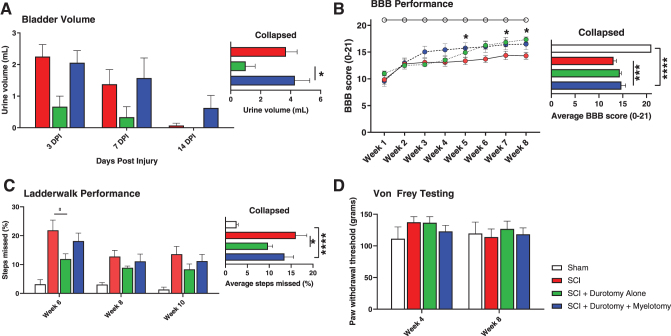
FIG. 4.
Surgical decompression promotes functional outcome after spinal cord injury (SCI). (A) Durotomy alone resulted in earlier bladder reflex recovery than durotomy plus myelotomy (p < 0.05). (B) As expected, all injured animals showed some degree of spontaneous recovery of their hindlimb open-field locomotion. Durotomy plus myelotomy led to significantly better Basso, Beattie, Bresnahan (BBB) scores overall compared with SCI control treatment (p < 0.001). Durotomy plus myelotomy animals showed accelerated locomotor recovery compared with durotomy alone animals. From 5 weeks onwards, durotomy plus myelotomy treated animals performed better than SCI control treated animals (p < 0.05). At 8-week follow-up, durotomy animals performed better than SCI control treated animals (p < 0.05). (C) The Ladder Walk test was administered to examine the sensory-induced hindlimb motor function. Durotomy alone resulted in a significant overall decrease in Ladder Walk error rate compared with control animals (p < 0.05). (D) Von Frey testing was performed to determine decompression-related changes of nociception in our study animals. No significant differences were found. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Color image is available online.