FIGURE 2.
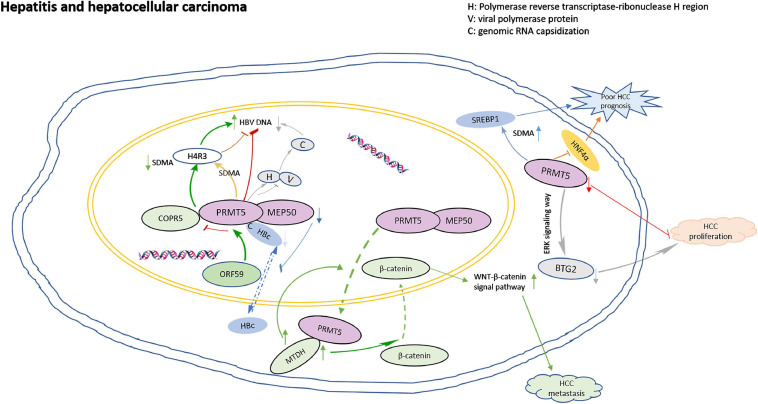
The model for PRMT5 roles in regulation of hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. ORF59 binds to the N-terminal domain of PRMT5, competitively destroying the binding of PRMT5 and COPR5, leading to the decrease of H4R3 SDMA levels and the increase of viral gene transcription; PRMT5 blocks polymerase by binding to the reverse transcriptase ribonuclease H region of the polymerase, interfering with the capsizing of genomic RNA; HBV core protein (HBc) interacts with PRMT5 and MEP50 through its C-terminal arginine-rich domain, and arginine methylation could regulate the nuclear to cytoplasmic shuttle of HBC protein. Down-regulation of PRMT5 and MEP50 decreased the level of HBC protein in nucleus. When MTDH is overexpressed in HCC cells, PRMT5 transfers from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and then β-catenin transfers from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, and the WNT-β-catenin signaling pathway is upregulated. MTDH-PRMT5 complex could promote the metastasis of HCC by regulating WNT-β-catenin signaling pathway. PRMT5 leads to the down regulation of tumor suppressor BTG2 expression through ERK pathway, and consequently accelerated HCC proliferation. PRMT5 antagonizes the expression of HNF4α and resulted in poor prognosis.