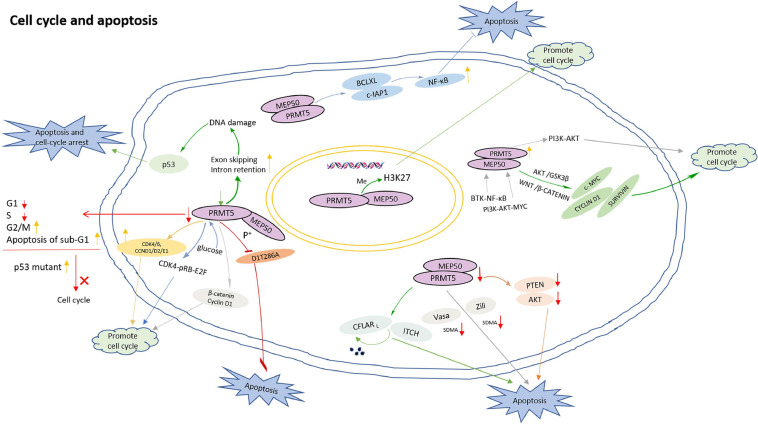
FIGURE 4.
The model for PRMT5 roles in regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis. PRMT5-mediated H3K27 methylation inhibition contributes to cell cycle progression; PRMT5 depletion caused an increase of sub-G1 cells during the DNA damage response; Loss of PRMT5 activity leads to endogenous DNA damage which triggers p53 activation and induces cell apoptosis; Compared with wild-type p53, a p53 mutant compromised in arginine methylation has altered effects on the cell cycle; PRMT5 inhibits cyclin D1T286A-induced apoptosis in a MEP50 phosphorylation-dependent manner; PRMT5 promotes cell cycle progression by up-regulating β-catenin, Cyclin D1, CDK4/6, and CCND1/D2/E1; PRMT5 inhibition resulted in a decrease in the proportion of cells in G1 and S phases, an increase in the proportion of cells in the G2/M phase, and an increase in apoptosis of sub-G1; By influencing the interaction between CFLARL and ITCH, PRMT5 regulates the polyubiquitination and degradation of CFLARL, regulating the apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells; PRMT5 interacts with Zili and Vasa, and directly catalyzes the SDMA of Vasa and Zili. The deletion of PRMT5 leads to the dysregulation of the expression of Vasa and Zili, and lead to germ cell apoptosis; When PRMT5 is inhibited, the down regulation of various signal molecules such as Akt and PTEN will induce apoptosis; PRMT5 can stimulate liver glucose metabolism, and activate CDK4-pRB-E2F-mediated transcription under glucose induction to promote HCC cell cycle progression; PRMT5 activates PI3K-AKT signaling and promotes cell cycle progression.