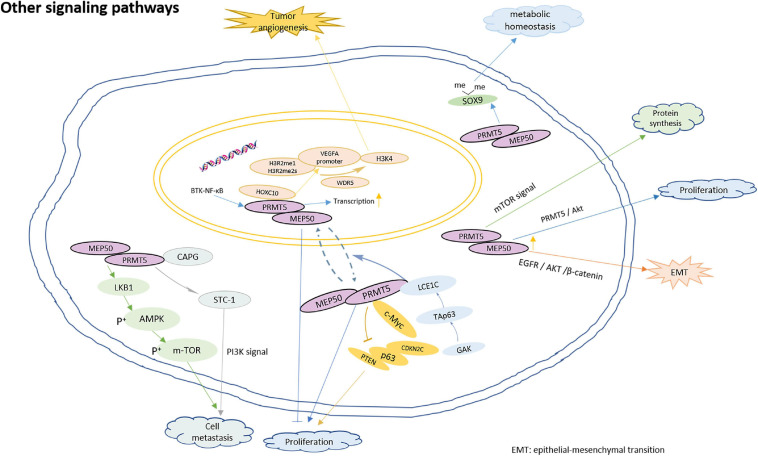
FIGURE 5.
The model for PRMT5 roles in regulation of other biological functions. PRMT5 interacts with LCE1C, and LCE1C promotes the cytoplasmic retention of PRMT5 or the transport of PRMT5 from nucleus to cytoplasm through direct interaction, thereby preventing cell proliferation; The direct binding of PRMT5 and c-Myc transcriptionally inhibits the expression PTEN, p63, CDKN2C, and so on, thus promoting the proliferation of gastric cancer cells; The depletion of PRMT5 activates mTOR signaling and increase protein synthesis in hematopoietic stem cells; PRMT5 interacts directly with HOXC10, promoting the enrichment of H3R2me1 and H3R2me2s on the VEGFA promoter, and recruiting WDR5 for subsequent methylation of H3K4 on the VEGFA promoter, which eventually leads to the transcription of VEGFA and promotes angiogenesis in glioma; PRMT5 promotes the metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma by activating Wnt4/β – catenin signaling pathway; PRMT5 directly binds to CAPG, and CAPG regulate STC-1 transcription by competing with PRMT5 to enhance breast cancer metastasis; Knocking down PRMT5 could inhibit tumor growth and lung metastasis by up-regulating the expression of LKB1 and p-AMPK, and down-regulating the expression of p-mTOR; overexpressed PRMT5 promotes EMT by activating EGFR/AKT/β-catenin signaling; PRMT5 could improve SOX9 stability by dimethylating the protein, which contributes to maintain the matrix metabolic homeostasis of the chondrocytes.