Figure 4. Dhps deletion reduces proinflammatory macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue and improves glucose tolerance during meta-inflammation.
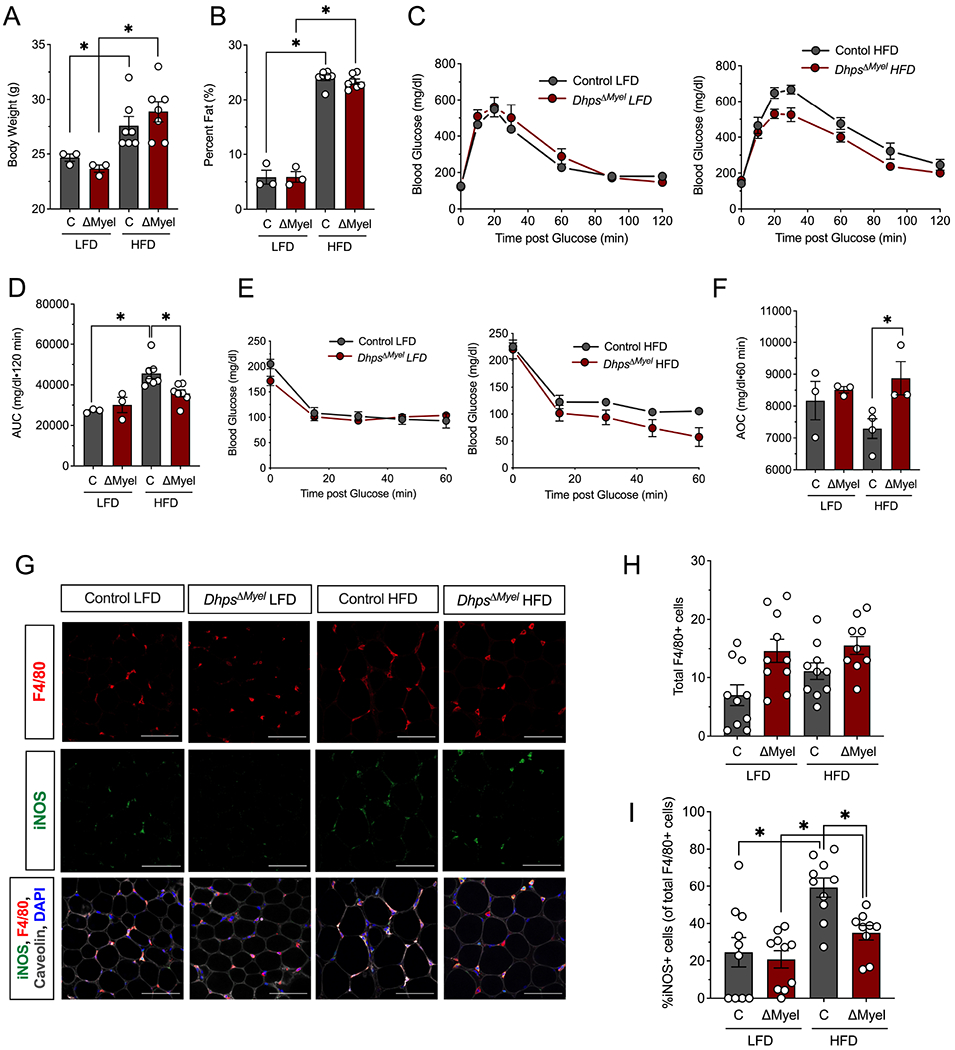
Control (combination of DhpsLoxp/Loxp and DhpsLoxp/+) and DhpsΔMyel male mice were fed a low fat diet (LFD, 10% kcal from fat) or a high fat diet (HFD-60% kcal from fat) (n=10 per group) for 5 weeks. (A) Body weight at end of study. (B) Percentage body fat at end of study as determined by EchoMRI. (C) Glucose tolerance tests (GTTs) at end of study (n=7 mice per group); (D) AUC analysis of GTTs. (E) Insulin tolerance tests (ITTs) at end of study; (F) AOC analysis of ITTs. (G) Representative immunofluorescence micrographs of epididymal adipose tissue stained for the proteins indicated (scale bar = 100 μm); (H) Quantification of the average number of F4/80+ cells per field of view (4 fields of view from each of 9-10 animals); (I) Quantification of the percent of adipose tissue resident M1 macrophages (iNOS+/F4/80+ cells) to total macrophages (F4/80+ cells) (n=3-7) *p<0.05 by ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
