Fig 1. C. albicans isolate 529L elicits less vaginal immunopathology.
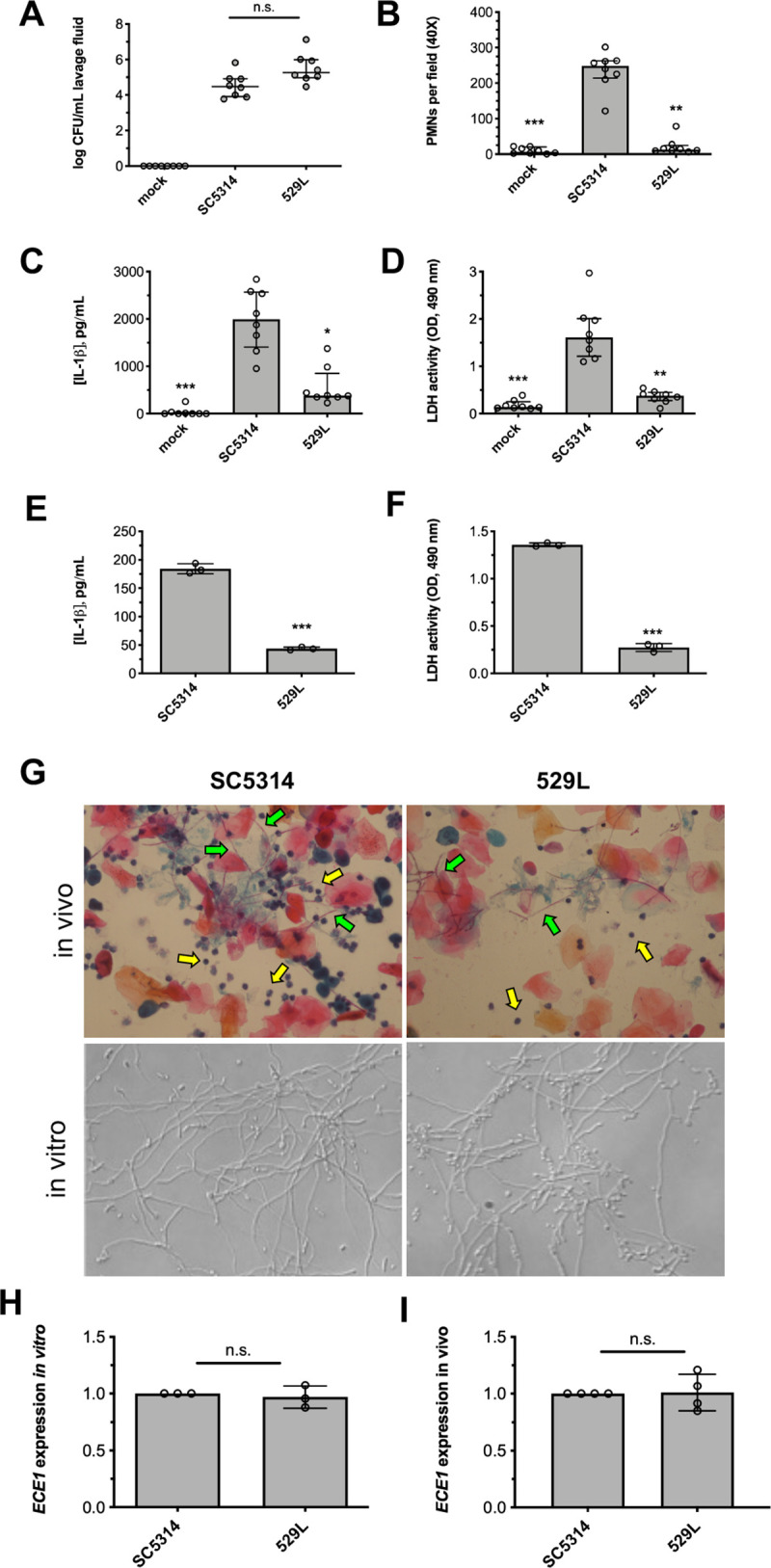
WT strain SC5314 and clinical isolate 529L were intravaginally inoculated into estrogen-treated C57BL/6 mice. Mice (n = 8 per group) underwent vaginal lavage at d 3 post-infection and lavage fluids assessed for (A) CFU by microbiological plating (median ± interquartile range), (B) PMN recruitment by microscopy (median ± interquartile range), (C) IL-1β by ELISA (median ± IQR), and (D) tissue damage by LDH assay (median ± IQR). Statistical significance was assessed using Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s post-test. A431 vaginal epithelial cells were challenged with C. albicans (0.01 MOI) for 24 h. Cell supernatants were assessed for (E) IL-1β release by ELISA (mean ± SD) and (F) LDH release (mean ± SD). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test. (G) Representative images of SC5314 and 529L during in vivo (vaginal lavage fluid) and in vitro (RPMI-1640) growth depicting filamentation (green arrows) and neutrophil recruitment (yellow arrows). (H) In vitro ECE1 expression levels were assessed by qRT-PCR 4 h after strains were transferred to RPMI-1640 and normalized to ACT1 expression values and SC5314 using the ΔΔCt method (mean ± SD). (I) In vivo ECE1 expression was assessed by qRT-PCR on vaginal lavage samples obtained at d 3 post-infection and normalized to ACT1 expression values and SC5314 using the ΔΔCt method (mean ± SD). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test. All in vitro experiments were conducted in biological triplicate. *, p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
