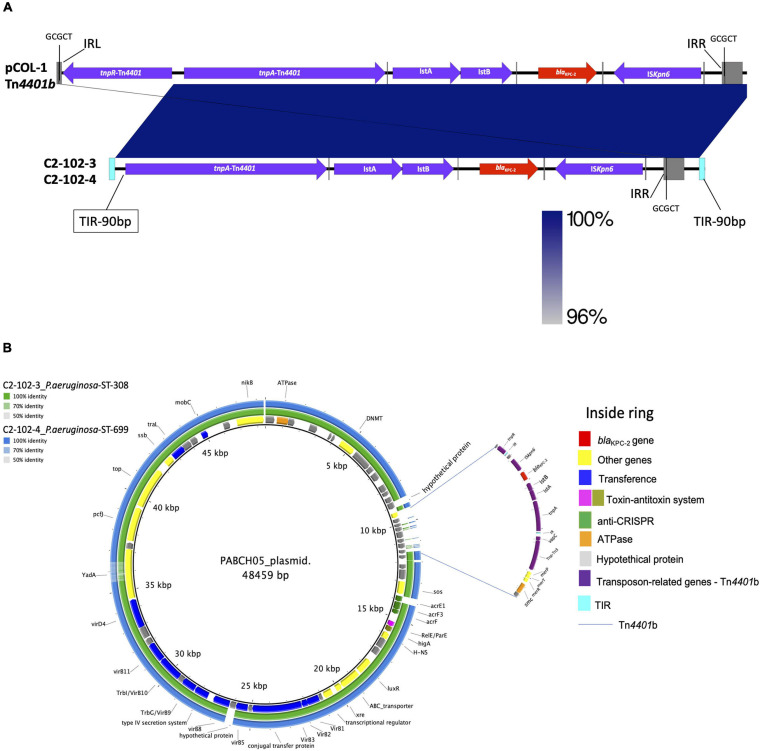
FIGURE 4.
(A) Comparison of Tn4401b containing blaKPC–2 gene identified in two isolates of P. aeruginosa from the same patient (C2-102-3 and C2-102-4) with isoform Tn4401b from P. aeruginosa COL-1 from Colombia (accession number KC609323.1) (18). Gray squares represent left and right inverted repeats (IRL and IRR, respectively) delimiting Tn4401b, flanked by GCGCT target site duplications (TSDs). Genes are denoted by horizontal arrows with their corresponding transcription orientations. Insertion sequences: Iskpn6 and Iskpn7 with IRL and IRR sequences (gray line); transposase tnpA and resolvase, tnpR. (B) BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG 0.95 and BLASTN v2.2.29) of comparison of the annotated plasmid from P. aeruginosa PABCH05 strain, Boston, MA, United States (accession number CP056099.1), with C2-102-3 and C2-102-4 isolates sequenced in this study. The internal ring shows the resistance and structural genes of the plasmid of the PABCH05 strain indicated by different colors (right panel). Green ring and blue ring correspond to the BLASTn result of C2-102-3 and C2-102-4 contigs relative to the plasmid reference (inside ring), respectively. The Tn4401b without the resolvase (tnpR) gene and surrounding is indicated by the blue lines. The transposon is flanked at both ends by terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) of 90 bp followed downstream by tnpR and upstream by vapC-tnpA-merP-merT-merR genes.