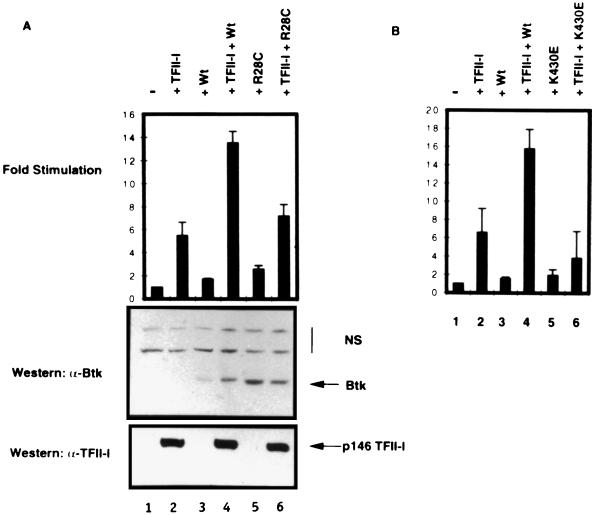
FIG. 1.
Wild-type Btk, but not mutant Btks, potentiates TFII-I-dependent transcriptional stimulation of Vβ 5.2 in COS7 cells. (A) Transient transfection of COS7 cells. Shown are basal-level expression of the Vβ 5.2 promoter (−, lane 1) and expression in the presence of ectopic TFII-I alone (+TFII-I, lane 2), wild-type Btk (+Wt, lane 3), or xid mutant Btk (+R28C, lane 5). Cotransfection of wild-type Btk with TFII-I (TFII-I + Wt, lane 4), but not xid mutant Btk with TFII-I (+TFII-I + R28C, lane 6), further potentiates TFII-I-mediated activation of the Vβ 5.2 reporter. Western blotting of transfection extracts with an anti-Btk antibody (α-Btk) or an anti-TFII-I antibody (α-TFII-I) demonstrates equivalent levels of ectopic TFII-I expression in the indicated lanes. NS, nonspecific bands. (B) Wild-type Btk, but not kinase-deficient (K430E) Btk, potentiates TFII-I-mediated stimulation of the Vβ 5.2 promoter. The Vβ 5.2 promoter basal expression (−, lane 1) is stimulated by TFII-I (+TFII-I, lane 2). Neither wild-type (+Wt, lane 3) nor K430E mutant (+K430E, lane 5) Btk affects Vβ 5.2 promoter expression independently. Cotransfection of TFII-I with wild-type Btk (TFII-I + Wt, lane 4) but not kinase-deficient Btk (+TFII-I + K430E, lane 6) further potentiates TFII-I-mediated activation of the Vβ 5.2 promoter.