Figure 1. Poly(I:C) induces histone extranuclear translocation via TLR3 in endothelial cells.
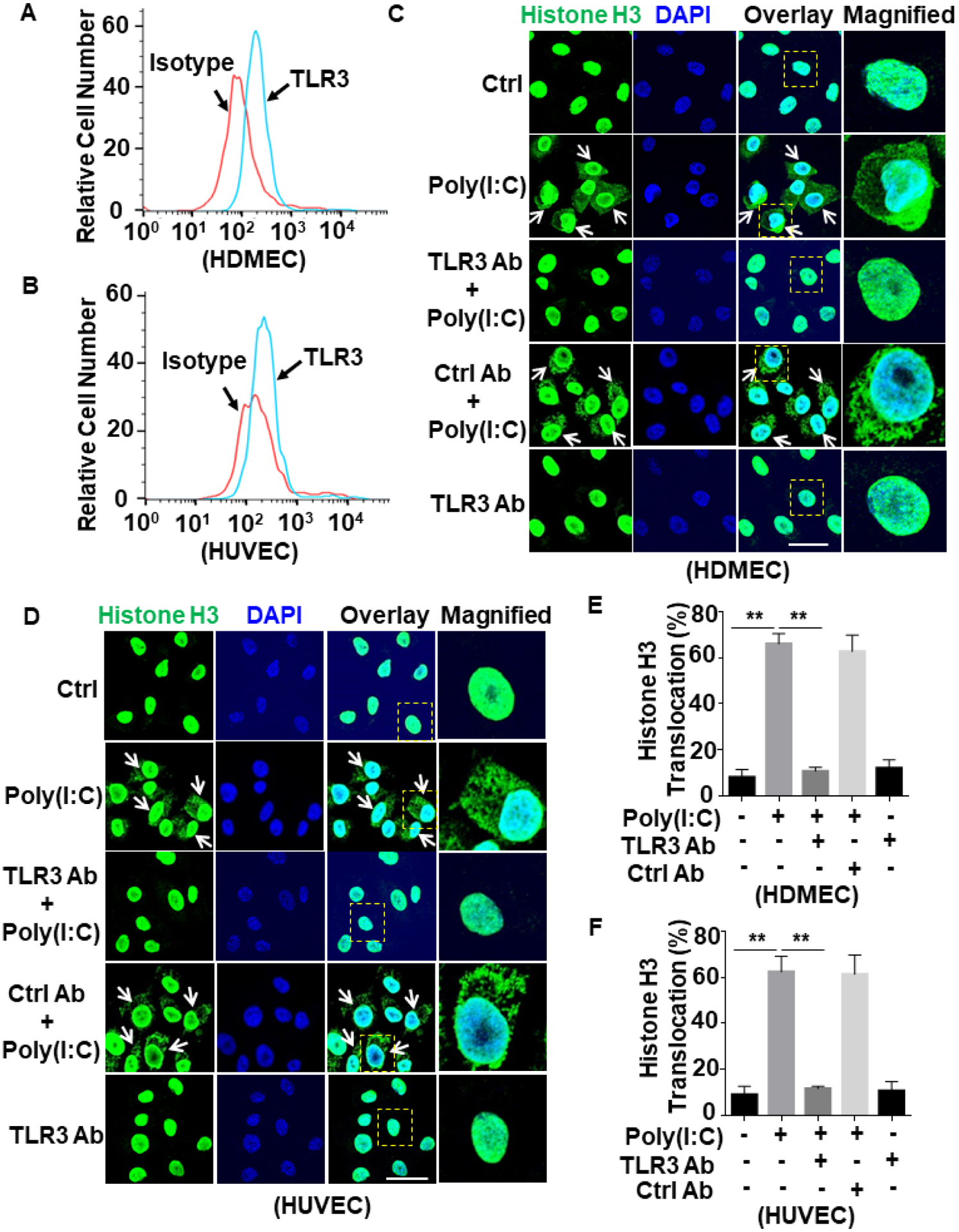
(A and B) Confluent HDMECs (A) or HUVECs (B) were stained with mouse anti-TLR3 antibody and FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The cell surface level of TLR3 was measured by flow cytometry. (C and D) HDMECs (C) or HUVECs (D) were pretreated with anti-TLR3 antibody or a control antibody (5 μg/mL for 1h) followed by stimulation with poly(I:C) (10 μg/mL for 1h). Cells were fixed and permeabilized followed by staining for histone H3 with mouse anti-histone H3 antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The nucleus was stained with DAPI. Immunofluorescence images were taken by confocal microscopy. Arrows indicate extranuclear translocation of histone H3. The magnified insets correspond to cells marked with yellow dashed boxes. (E and F) The quantitation of poly(I:C)-mediated translocated cells from the nucleus to the extranuclear space for HDMECs (C) and HUVECs (D). Scale bar: 20 μm. Results are shown as means ± standard error from at least 3 independent experiments. **p < 0.01. Ctrl, control.
