Figure 3. APC inhibits poly(I:C)-induced histone extranuclear translocation and extracellular trap formation in macrophages.
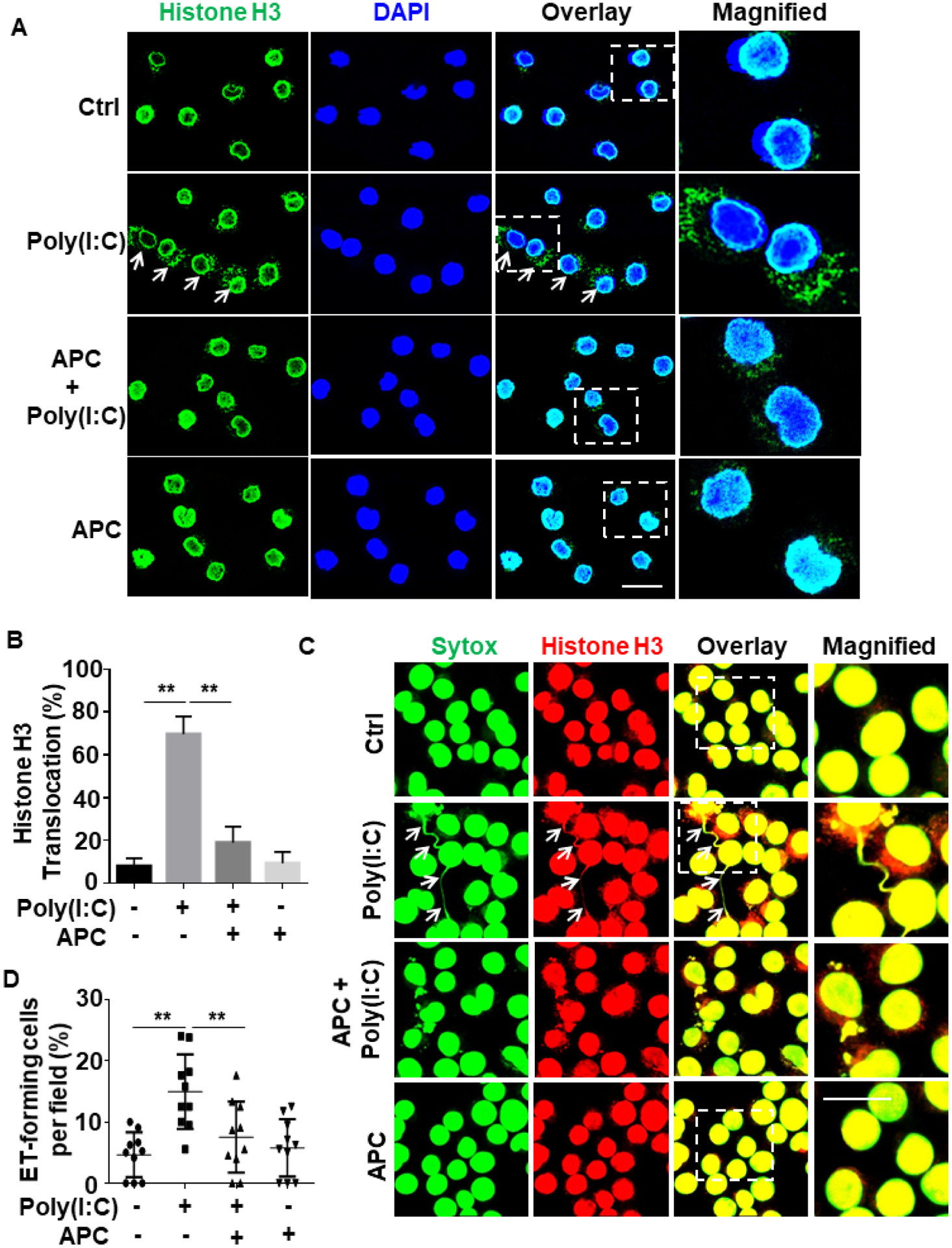
(A) J774A.1 macrophages were pretreated with APC (20 nM for 3h) followed by stimulation with poly(I:C) (10 μg/mL for 1h) (APC remained in the media after addition of poly(I:C)). Cells were fixed and permeabilized, followed by staining for histone H3 with mouse anti-histone H3 antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The nucleus was stained with DAPI. Immunofluorescence images were taken by confocal microscopy. Arrows indicate extranuclear translocation of histone H3. (B) The quantification of poly(I:C)-mediated translocated cells from the nucleus to the extranuclear space for J774A.1 macrophages. (C) J774A.1 macrophages were pretreated with APC (20 nM for 3h) followed by stimulation with poly(I:C) (10 μg/mL for 4h). Cells were fixed and permeabilized, followed by staining for histone H3 with mouse anti-histone H3 antibody and Alexa Fluor 555-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. DNA was stained with Sytox Green. Immunofluorescence images were taken by confocal microscopy. Arrows indicate cells with extracellular trap formation. The inset boxes from each group are magnified. (D) The quantitation of ET-forming cells in (C). All experiments were repeated at least three times. **p < 0.01. Ctrl, control. Scale bar: 20 μm.
