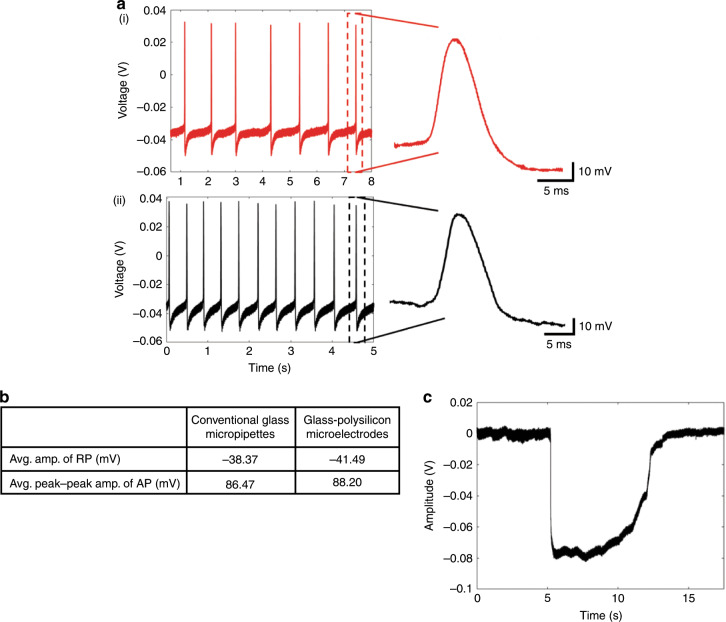
Fig. 2. Intracellular recordings using the glass–polysilicon (GP) microelectrode.
a (i) Intracellular recordings (RP = −35.5 mV, peak–peak AP = 80.1 mV) obtained from an isolated abdominal ganglion neuron in Aplysia using a conventional glass micropipette and (ii) using GP microelectrode (RP = −38.8 mV, peak–peak AP = 85.5 mV). b Comparison of the quality of intracellular signals using GP microelectrodes with those obtained using conventional glass micropipettes (n = 3 neurons) showing no significant difference (RP: p > 0.5, AP: p > 0.2). c In vivo intracellular recording (RP = −74 mV) obtained from the motor cortex of a rat using a GP microelectrode (RP resting potential, AP action potential).