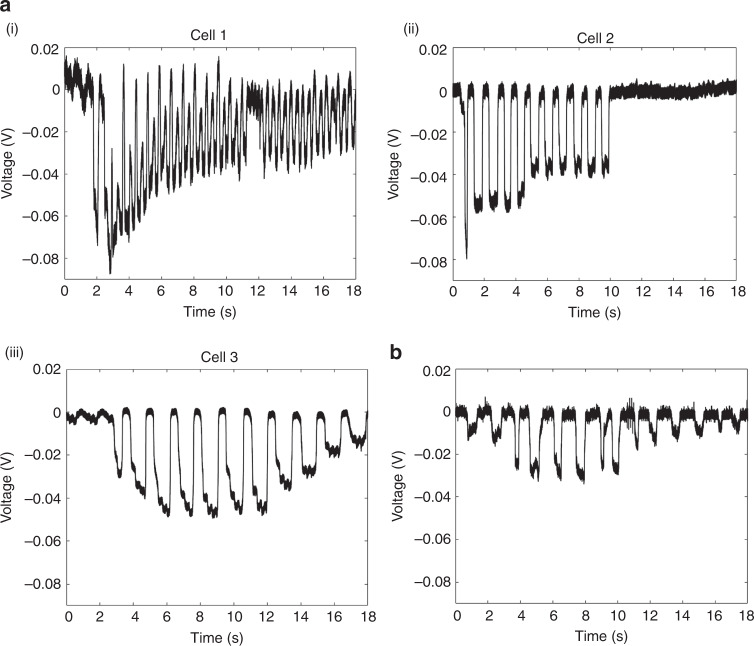
Fig. 7. In vivo cortical recordings.
a Automated intracellular potentials obtained from three different cells in the rat motor cortex after integration of the controller with a GP microelectrode and a conventional hydraulic microdrive. The recordings showed resting membrane potentials in the order of −50 to −65 mV along with large, periodic fluctuations due to brain pulsations caused by breathing (~0.5–1 Hz) and vascular pulsations (~4 Hz). b Autonomous intracellular recording obtained from a cell in the rat motor cortex with the fully integrated robotic, MEMS-based intracellular recording system. The resting potential was −30 mV, probably due to inadequate seal between the GP microelectrode and cell. Large, periodic fluctuations in the resting membrane potential were observed due to brain pulsations caused by breathing (~0.7 Hz).