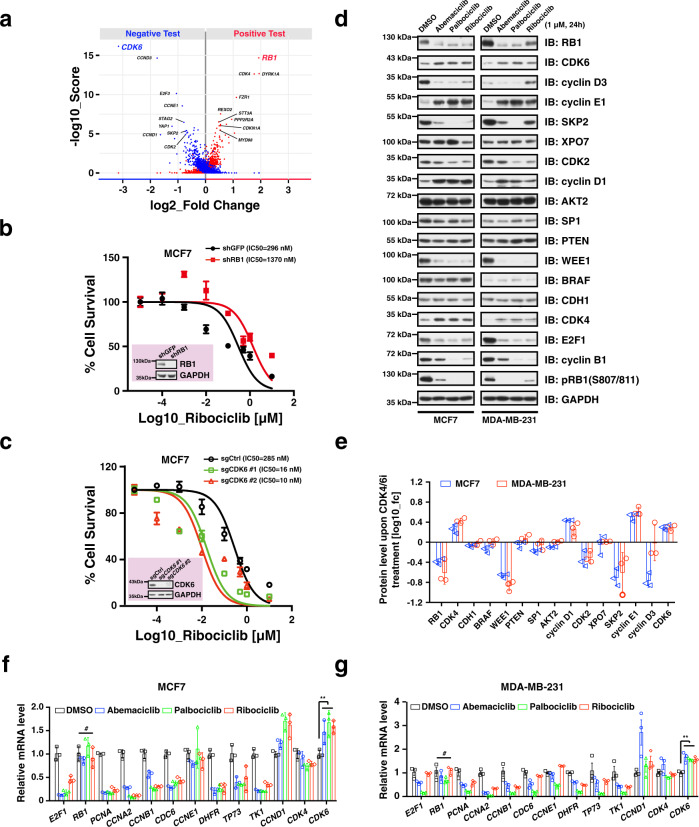
Fig. 1. CDK4/6i treatment leads to dysregulation of RB1 and CDK6 to drive acquisition of CDK4/6i resistance in breast cancer.
a Volcano plot showing drivers of CDK4/6i resistance. MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were infected by a pooled CRISPR library. Cells stably expressing sgRNA were then cultured for 21 days in the presence of DMSO and ribociclib (0.5 μM), respectively. gRNAs at day 0 and day 21 were amplified by PCR and determined by Illumina deep-sequencing. The P values were based on the empirical Bayes modulated t-statistics. b Knocking-down of RB1 drives resistance of MCF7 cells to ribociclib treatment (n = 4). c Knocking-out of CDK6 sensitizes MCF7 cells to ribociclib treatment (n = 4). d Immunoblot showing the protein levels of cell cycle genes in response to CDK4/6i treatment in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines. e Quantification of protein intensity of cell cycle genes in (d) (n = 3). The quantification was performed using ImageJ (1.48 v) software. f RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of indicated cell cycle genes in the context of CDK4/6i treatment (1 μM, 24 h) in MCF7 breast cancer cells (n = 3). The P values were calculated by Student’s t-test (two-sided). #: no significance, **P < 0.01. g RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of indicated cell cycle genes in the context of CDK4/6i treatment (1 μM, 24 h) in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells (n = 3). The P values were calculated by Student’s t-test (two-sided). #: no significance, **P < 0.01. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. The relevant raw data and uncropped blots are provided in Source Data.