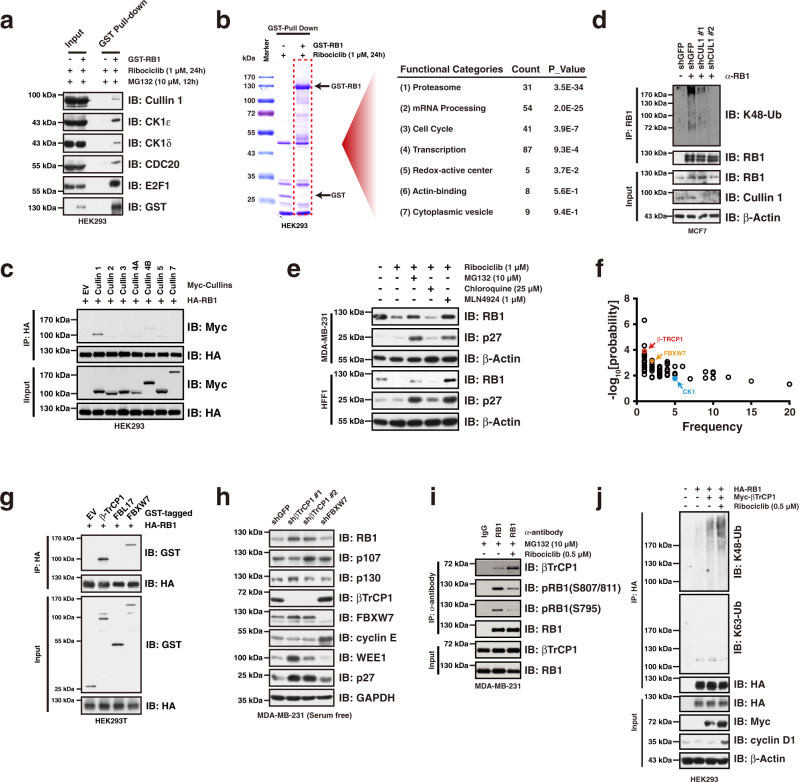
Fig. 2. βTrCP1 mediates RB1 for proteasomal degradation upon CDK4/6i treatment.
a Immunoprecipitation assay validating the interaction between RB1 and its interacting proteins identified by LC-MS/MS. b Gene functional classification of RB1-MS results showing that proteasome related proteins were significantly enriched in the GST-RB1 precipitates upon CDK4/6i treatment. Functional categories analysis was performed by the DAVID tools (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp). The P values associated with each annotation terms inside each cluster were determined by Fisher Exact test. c Immunoprecipitation assay showing RB1 specifically interact with Cullin 1 in cells. d Knocking-down of Cullin 1 diminished K48-linked polyubiquitination of RB1 in MCF7 cells. e Exposure of HFF1 and MDA-MB-231 cells with MG132 and MLN4924 blocked ribociclib treatment induced RB1 reduction. f Eukaryotic Linear Motif (ELM) prediction of RB1 protein showing that βTrCP1, FBXW7, and CK1 are potential RB1 interacting proteins. The prediction was performed by the tool of The Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource for Functional Sites in Proteins (http://elm.eu.org/index.html). g Immunoprecipitation assay showing that βTrCP1 and FBXW7 physically interacted with RB1 in cells. h Knocking-down of βTrCP1, but not FBXW7, led to RB1 accumulation in the context of serum starvation in MDA-MB-231 cells. i Immunoprecipitation assay showing that ribociclib treatment facilitated the interaction between RB1 and βTrCP1. j Ectopic expression of βTrCP1 elevated K48-linked polyubiquitination of RB1 in cells. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. The relevant raw data and uncropped blots are provided in Source Data.