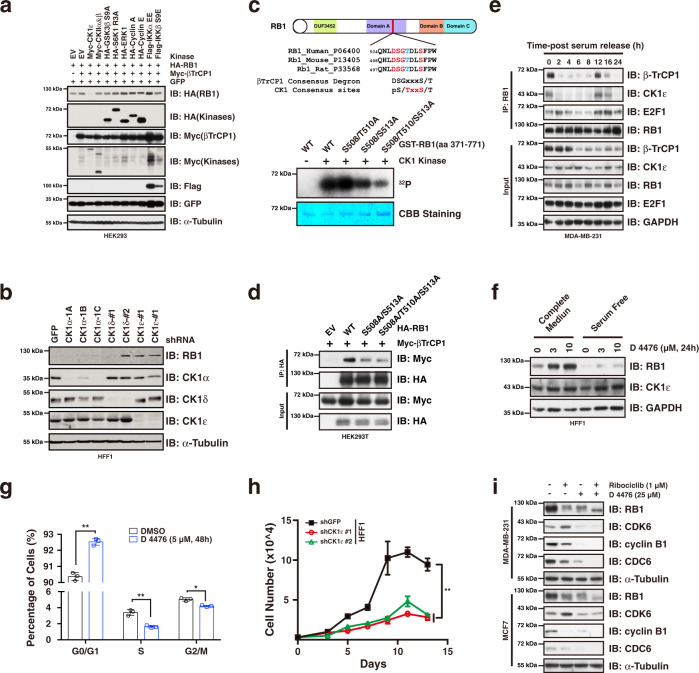
Fig. 3. Phosphorylation of RB1 by CK1ε promotes βTrCP1-mediated degradation.
a Ectopic expression of CK1ε led to reduced RB1 protein abundance. b Knocking-down of CK1ε resulted in RB1 accumulation in HFF1 cells. c In vitro kinase assay showing that CK1ε can phosphorylate RB1 at S508/T510/S513 sites. d Immunoprecipitation assay showing that mutation of the CK1ε phosphorylation sites of RB1 diminished its interaction with βTrCP1. e Immunoprecipitation assay showing that RB1 specifically interacted with βTrCP1 and CK1ε in G1 phase. MDA-MB-231 cells were serum starved for 48 h followed by serum re-addition and harvested at indicated time points. f Inhibition of CK1ε kinase using CK1 inhibitor D 4476 led to RB1 accumulation in a dose-dependent manner in HFF1 cells. g Employment of D 4476 led to increased cell population in G1 phase in HFF1 cells (n = 3). The P values were calculated by Student’s t-test (two-sided). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. h Knocking-down of CK1ε suppressed HFF1 cell proliferation (n = 4). Statistical differences were assessed by two-way ANOVA (two-sided). **: P < 0.01. i Combination of D 4476 prevented ribociclib treatment induced RB1 degradation and CDK6 accumulation in MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cells. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. The relevant raw data and uncropped blots are provided in Source Data.