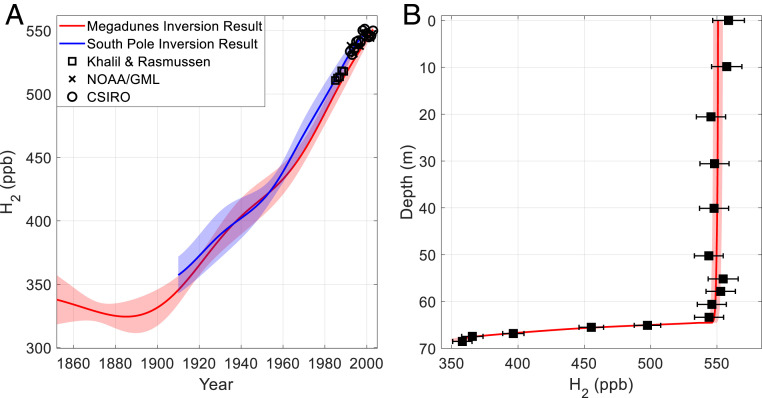
Fig. 1.
Reconstructions of atmospheric H2 and associated Megadunes firn air depth profiles. (A) Red line and shading—mean inferred atmospheric history and ±1σ uncertainty from 4,000 Monte Carlo inversions on the Megadunes firn air measurements (see Firn Air Model Inversion and Recovering the Atmospheric History) using α = 8*10−2; blue line and shading- inferred atmospheric history and ±1σ uncertainty from a South Pole firn air reconstruction (22); and black squares, black x’s, and black circles—observed atmospheric H2 annual means from high southern latitude sites from 1985 to 1989 and 1992 to 2003 (2, 13, 17, 18); (B) Black squares and error bars—depth-averaged Megadunes firn air H2 measurements corrected for detector nonlinearity, calibration drift, and gravitational fractionation as described in SI Appendix. Error bars are the propagated ±2% measurement uncertainty; red line and shading show the mean modeled H2 depth profile and ±1σ uncertainty resulting from the inferred atmospheric history plotted in red in A.