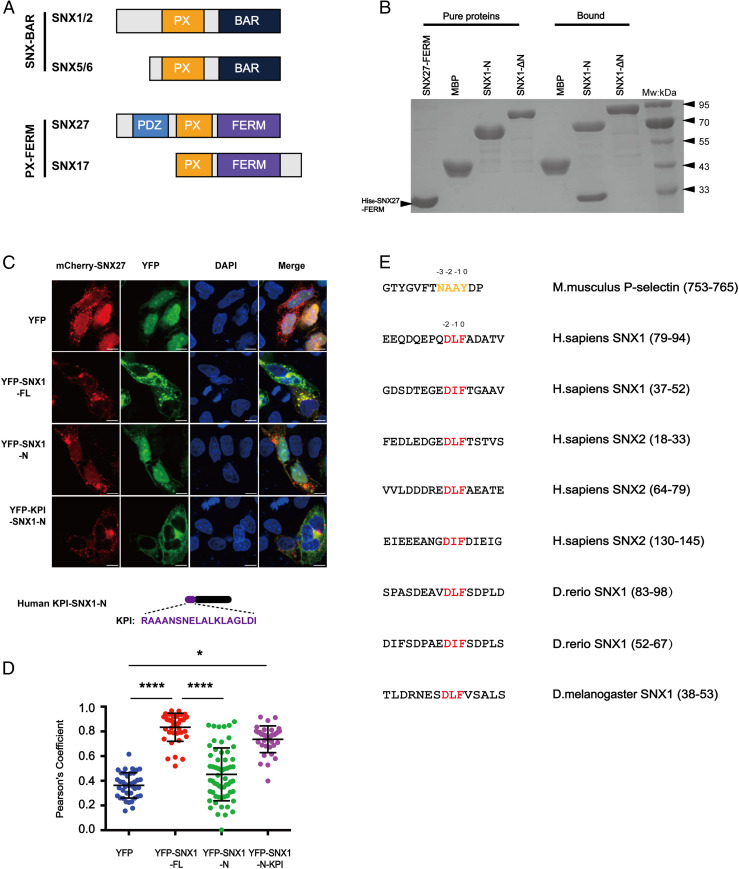
Fig. 1.
SNX27 specifically binds to multiple motifs centered on DLF within the N termini of SNX1/2. (A) Domain architecture of SNX-BAR and SNX-FERM proteins used in this study. PX, BAR, FERM (band4.1-ezrin-radixin-moesin), and PDZ (postsynaptic density 95-discs large-zonula occludens). (B) MBP-SNX1-N, SNX1-ΔN, and MBP pull-down of purified His-tagged SNX27 FERM. Shown is a Coomassie Blue–stained sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS/PAGE) gel with purified proteins (Left) and bound samples (Right). (C) Steady-state localization of different YFP-SNX1 constructs. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with mCherry-SNX27 (red) and YFP or YFP-SNX1 (green). A schematic diagram of KPI-SNX1-N is present on the bottom. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (D) Colocalization of mCherry-SNX27 and YFP in cells in C. Each dot represents Pearson’s correlation coefficients from one cell. Data were presented as mean ± SD, and P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001. (E) Sequence alignment of multiple fragments from the N termini of SNX1 and SNX2 highlights a DLF motif. Red color indicates the conserved DLF or DIF residues. The NPxY/NxxY motif in P-selectin is colored in orange and used for comparison.