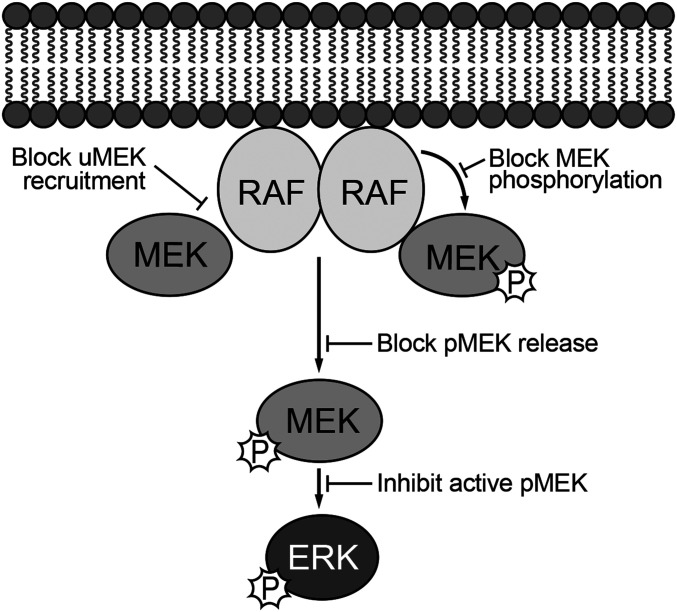
Fig. 4.
Paradigm for understanding the mechanisms of action of allosteric MEK inhibitors. Allosteric inhibitors could in principle act on free uMEK to interfere with its recruitment to RAF or on RAF-MEK complexes to block or alter phosphorylation of MEK by RAF or its release from RAF once phosphorylated. Allosteric MEK inhibitors could also inhibit free, active pMEK. We find that all inhibitors studied here act most potently on BRAF/MEK1 complexes in which they inhibit the dual phosphorylation of MEK that is required for its activation. Inhibition of active pMEK was also observed but with variable and sometimes dramatic loss of potency.