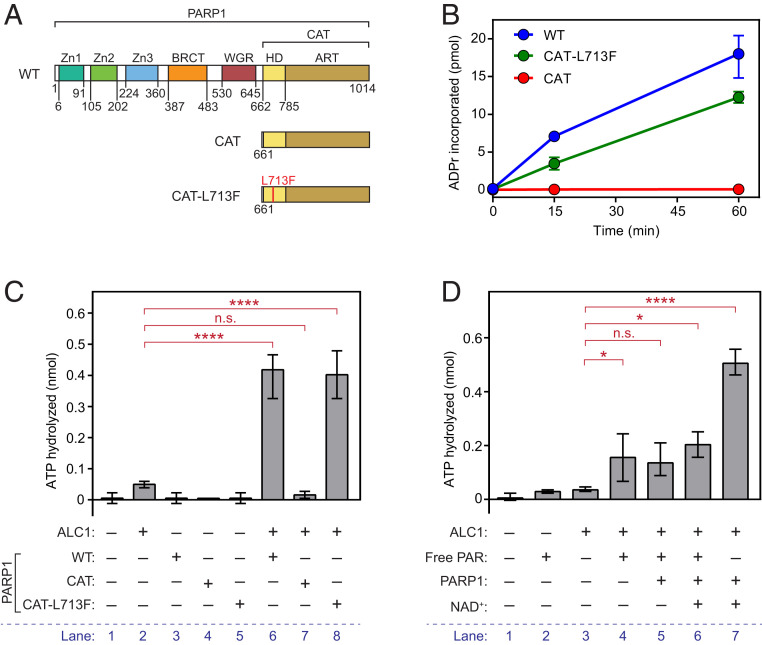
Fig. 1.
The PARP1 noncatalytic domains are dispensable for activation of ALC1 ATPase. (A) Diagram showing domain architecture of wild-type (WT) PARP1 and CAT mutants. (B) PARylation activities of WT PARP1, CAT-L173F, and CAT. Incorporation of 32P-NAD+ into PAR was assayed in the presence of nucleosomes and quantitated by liquid scintillation counting. Data represent ADP-ribose incorporation (mean ± range) calculated from at least two independent replicates. (C) ALC1 ATPase activity in the presence of WT PARP1 or PARP1 CAT mutants was assayed as described. Each reaction contained nucleosomes and NAD+. (D) ALC1 ATPase activity in the presence of 1 µM free PAR (Trevigen 4336-100-01), PARP1, and/or NAD+ was assayed as described. Each reaction contained nucleosomes. For C and D, data presented are values of mean ± range from at least two independent experiments. Significance was determined using Tukey’s multiple comparison test. n.s., not significant; *P < 0.05; ****P < 10−4.