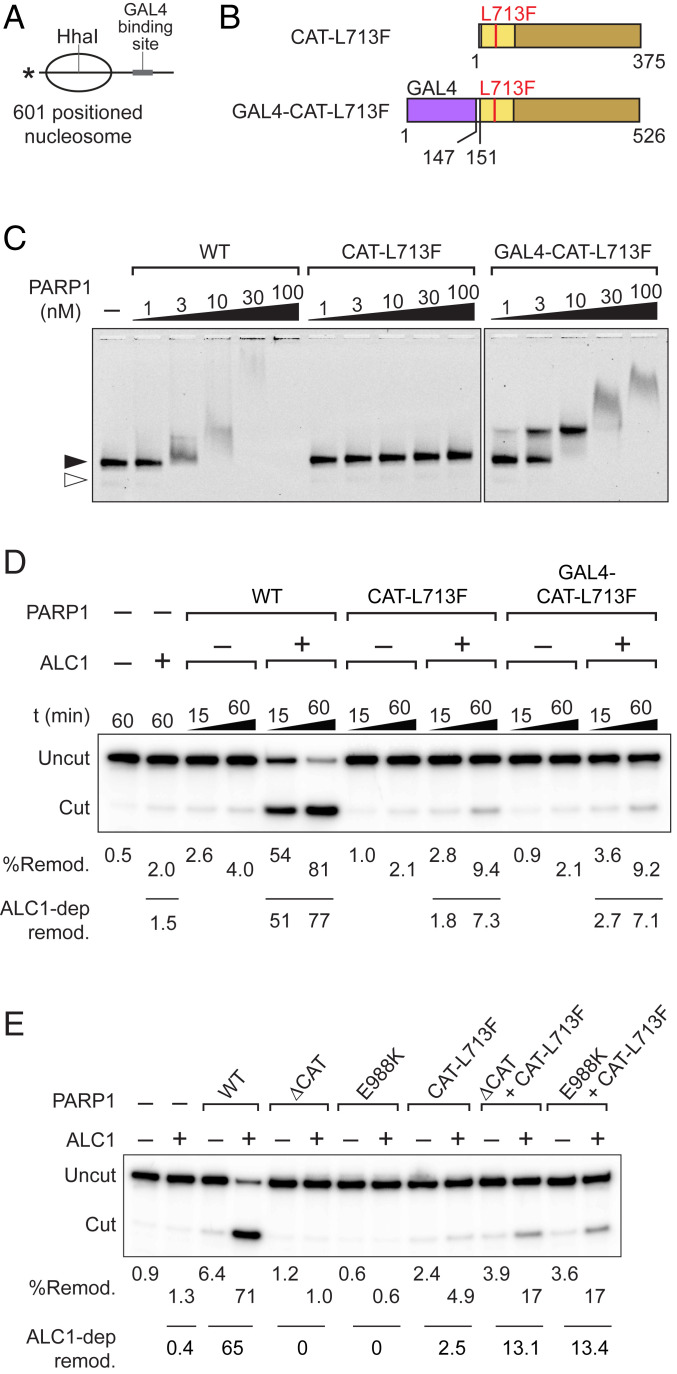
Fig. 5.
Tethering CAT-L713F to nucleosomes fails to restore ALC1-dependent nucleosome remodeling. (A) Diagram of laterally positioned nucleosome showing the position of the GAL4 binding site sequence centered in the 69-bp linker DNA. (B) Diagram of GAL4-CAT-L713F mutant. (C) Nucleosome binding of GAL4-CAT-L713F assayed by agarose gel electrophoresis and fluorescence imaging. Filled and open arrowheads mark the position of nucleosomes and free DNA, respectively. (D) Nucleosome remodeling assay to test activation of ALC1-dependent nucleosome remodeling by GAL4-CAT-L713F. (E) Nucleosome remodeling assay to test activation of ALC1-dependent nucleosome remodeling by a combination of PARP1ΔCAT or PARP1-E988K and CAT-L713F mutants. D and E show results of the same type of HhaI deprotection assay and phosphorimaging, but reactions shown in E were incubated for only 30 min. In both panels, total level of nucleosome remodeling of each reaction calculated from a fraction of the HhaI cut is shown underneath the gel image, whereas levels of ALC1-dependent nucleosome remodeling are listed below the lines. Remod., remodeling.