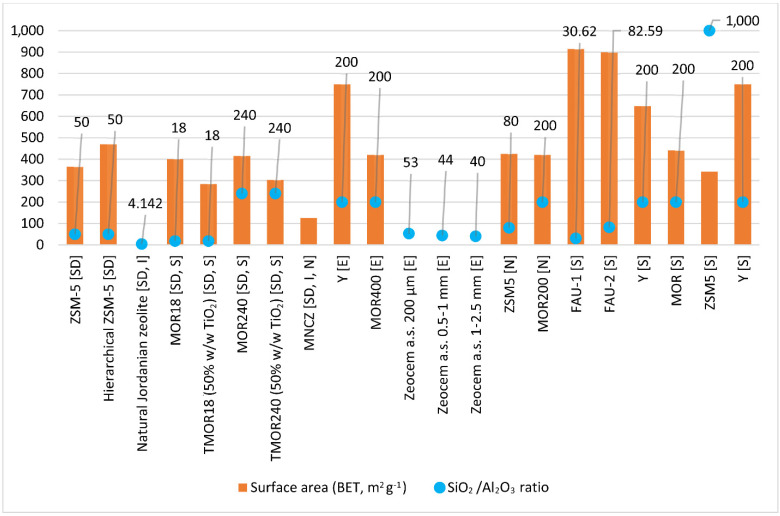
Figure 3.
Structural properties of zeolites described in the literature for the removal of selected NSAIDs ([SD]—sodium diclofenac, [I]—ibuprofen, and [N]—naproxen) and selected antibiotics ([E]—erythromycin and [S]—sulfamethoxazole), ZSM-5 [SD], hierarchical ZSM-5 [SD]—[157]; natural Jordanian zeolite [SD, I]—[159] MOR18 [SD, S], TMOR18 (50% (w/w) TiO2) [SD, S], MOR240 [SD, S], TMOR240 (50% (w/w) TiO2) [SD, S]—[162]; MNCZ [SD, I, N]—[163]; Y [E], MOR400 [E]—[98]; Zeocem a.s. 200 μm [E], Zeocem a.s. 0.5–1 mm [E], Zeocem a.s. 1–2.5 mm [E]—[164]; ZSM-5 [N], MOR200 [N]—[99]; FAU-1 [S], FAU-2 [S]—[62]; Y [S], MOR [S], ZSM-5 [S]—[165]; Y [S]—[166].