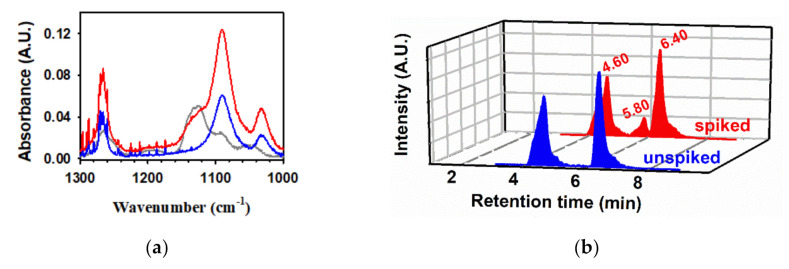
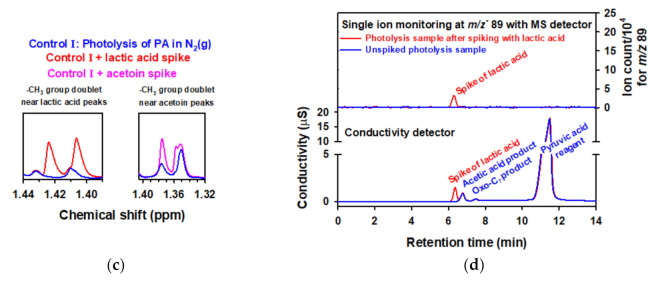
Figure 5.
(a) Infrared spectrum of (blue line) gas products collected over 50 mM aqueous PA after photolysis (λ > 305 nm) for 1 h, (gray line) acetoin standard, and (red line) gas product spiked with acetoin clearly demonstrating the absence of this molecule in the headspace of the reactor [83]; (b) extracted ion (m/z− = 267) chromatogram obtained by ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization(−)/MS (blue line) before and (red) after spiking the photolyzed PA sample for a final concentration of 20 μM acetoin prior to derivatization to form hydrazones. Retention times for the two hydrazones of PA are 4.60 and 6.40 min, and for the hydrazone of acetoin is 5.80 min (only observable in the spiked sample) but absent in the unspiked chromatogram [83]. (c) To the left hand-side is the 1H NMR spectrum for (blue), the −CH3 group doublet centered at ∼1.42 ppm in a control with 100.1 mM PA at pH 1.0 photolyzed at λ ≥ 305 nm for a 50% reagent conversion under continuous sparging with N2(g), and (red) the mismatch for this doublet after spiking to final concentration of lactic acid of 9.34 mM. To the right hand-side is the 1H NMR spectrum for (blue), the −CH3 group doublet centered at ∼1.36 ppm in the same control in left hand-side, and (pink) the mismatch for this doublet after spiking to an acetoin final concentration of 10.02 mM. This quality assurance analysis clearly demonstrated that lactic acid and acetoin are not photoproducts when working with well purified PA [77]. (d) At the bottom, the ion chromatogram is shown with conductivity detection for the region of elution of lactic acid for a control with 99.22 mM pyruvic acid at pH 1.0 photolyzed at λ ≥ 305 nm for a 21% reagent conversion under continuous sparging with N2(g) (blue) before and (red) after spiking to a final lactic acid concentration of 14.9 μM. The anions of all species were assigned with available standards and/or using the m/z− values obtained by tandem mass spectrometry. At the top, the extracted ion chromatogram for lactic acid is shown (m/z− 89) (blue) before and (red) after spike addition of lactic acid for the same samples in the bottom part of this panel, which completely discard the photoproduction of lactic acid when working with well purified PA [77]. Panels a and b: Copyright 2013, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Panels c and d: Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.