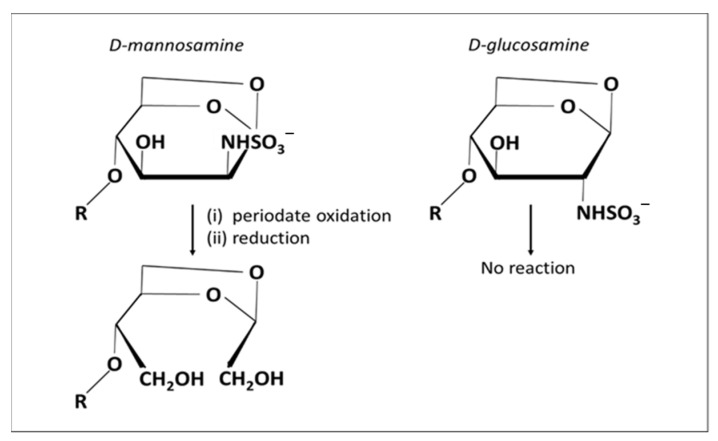
Figure 5.
Terminal 1,6-anhydro-D-mannosamine residues (upper left) formed during depolymerization under basic conditions, during enoxaparin manufacture, are oxidized by periodate to cleave the carbon to carbon (C2-C3) bond. The aldehydes formed can be reduced further to alcohols (lower right). Terminal 1,6-anhydro-D-glucosamine residues (upper right) in enoxaparin are not susceptible to periodate oxidation.