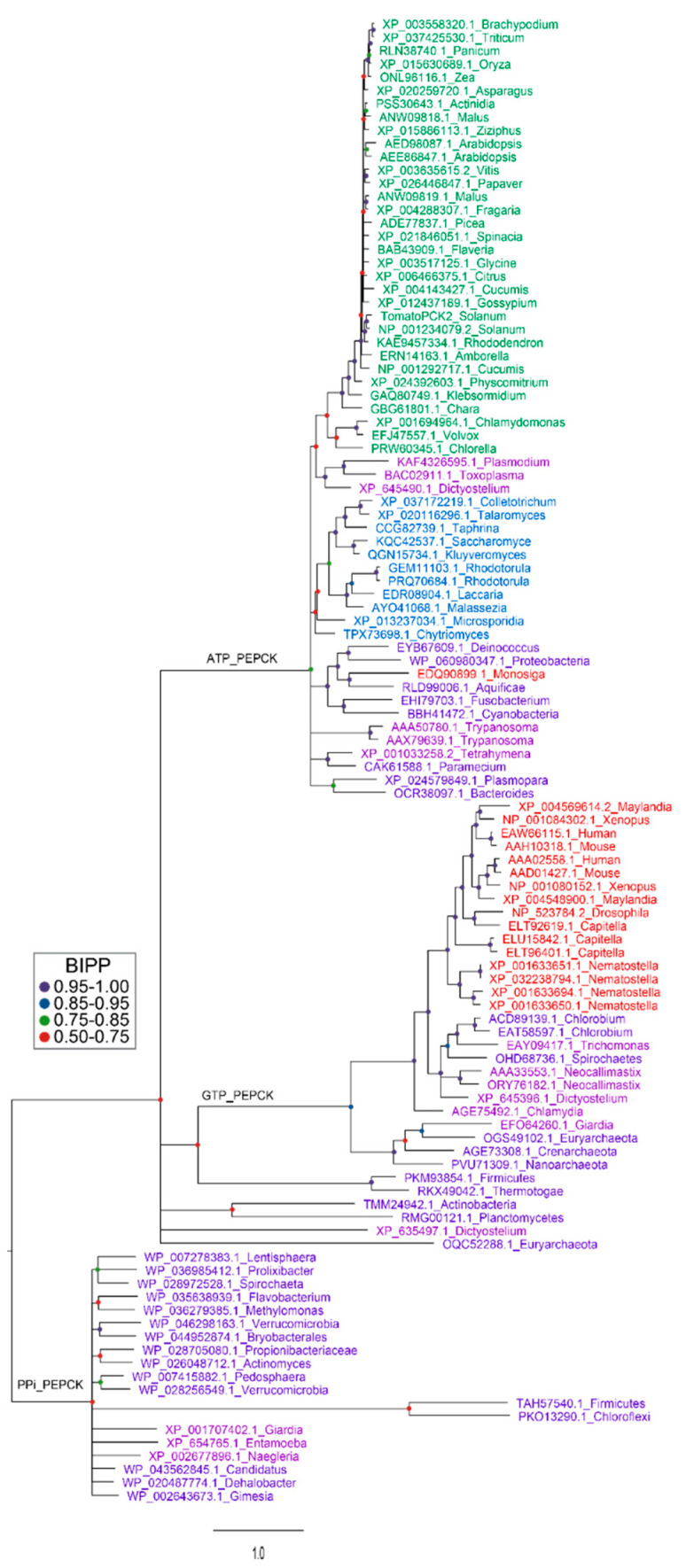
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of PEPCK proteins from three domains of life. Several representative PEPCK protein sequences were selected for each phylum of three domains of life [130] including bacteria [131,132], protozoans and fungi [133], plants [134] and metazoans in the NCBI database. Protein sequences were aligned using Clustal W [135]. After deletion of segments with poor consensus alignment, sequences were subjected to Bayesian inference for establishment of phylogenetic relationships between proteins [136]. Analysis were run for 5 million generations under a mixed amino-acid model with rate variation between sites estimated by a gamma distribution. Bayesian inference posterior probabilities (BIPPs) of tree nodes are indicated by coloured dots. Gene identifiers of the proteins are color-coded to represent the phyla from which they are derived. Green for plants, blue for fungi, pink for protozoans, purple for bacteria and red for metazoans. Corresponding species names are listed by the side of accession number on each branch of the tree. Note for the plant species there are very little differences in the amino acid sequence of the protein apart from in the c12 kD N-terminal extension. Thus, the reconstructed phylogeny of the plant enzyme is based largely on this part of the protein.