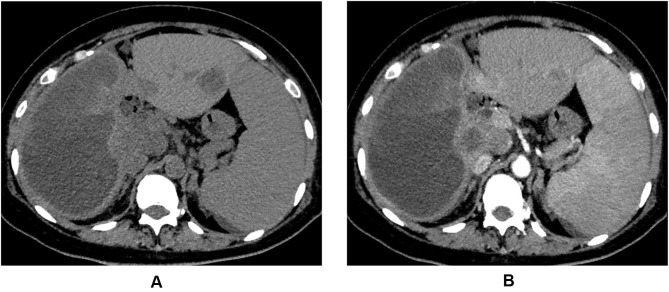
Figure 1.
A 43-year-old patient who received transarterial chemoembolization combined with molecular targeted agents plus immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma presented with abdominal pain and fever. The computed tomography plain scan (A) and enhanced scan (B) images of a patient demonstrated obvious liquefactive necrosis within the tumor (the right lobe of the liver). Catheter drainage was performed under the guidance of ultrasound and the bacterial culture result of the liquefactive necrosis content was positive.