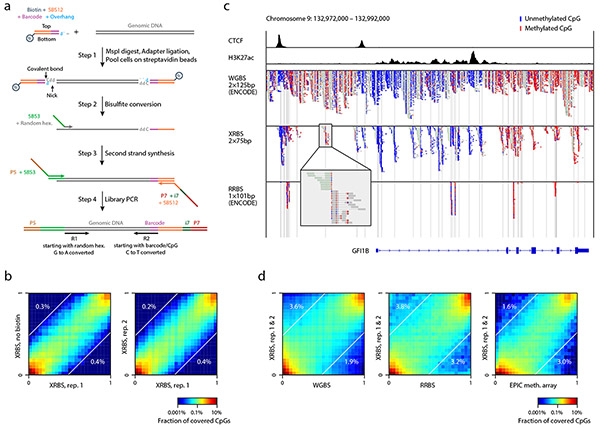
Fig. 1 ∣. An extended representation DNA methylation profiling method compatible with low input samples.
A) Schematic of extended representation bisulfite sequencing (XRBS). Barcoding samples in a single well through sequential lysis, digestion, and ligation minimizes DNA loss. Binding biotinylated adapters to streptavidin beads enables multiple samples to be combined into a single bisulfite conversion reaction, minimizing batch effects introduced during conversion. Random hexamer-primed second strand synthesis recovers fragmented DNA. PCR amplification yields sequencing libraries.
B) Heatmaps compare individual CpG methylation values acquired by XRBS with or without biotinylated adapters (left, Pearson’s r=0.96), and between technical replicates (right, r=0.97) for K562 cells. Percentages indicate the fraction of CpGs that differed between conditions (difference in beta-values >0.5). Analysis limited to CpGs with at least 15-fold coverage (n=313,330 and 721,760 CpGs).
C) Genome plot for the GFI1B gene locus compares read coverage between XRBS and public WGBS and RRBS datasets for K562 cells. Boxes represent reads, and unmethylated (blue) and methylated (red) CpGs are indicated. CTCF and H3K27ac ChIP-seq tracks reveal functional elements. Vertical grey lines mark MspI restriction sites. Insert shows XRBS reads flanking an isolated MspI site, which is not covered by RRBS.
D) Heatmaps compare individual CpG methylation values between XRBS and public WGBS (r=0.91), RRBS (r=0.90), or EPIC methylation array (r=0.90) datasets for K562 cells. Percentages indicate the fraction of CpGs that differed between conditions (difference in beta-values >0.5).