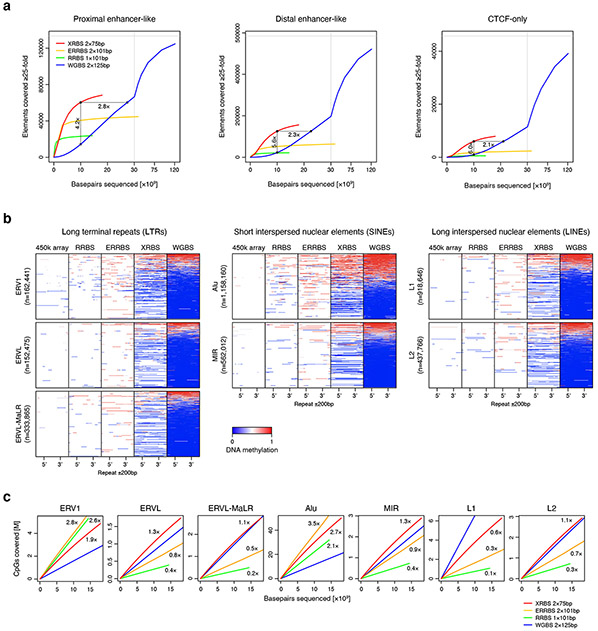
Extended Data Fig. 3 ∣. XRBS efficiently covers CpGs in regulatory elements and repetitive regions.
A) Plots show the number of proximal enhancer-like, distal enhancer-like, and CTCF-only elements (as defined in the ENCODE SCREEN database) with at least 25-fold combined coverage as a function of sequencing depth for XRBS (red), WGBS (blue), ERRBS (orange), and RRBS (green). Enrichment for functional elements at a uniform sequencing depth of 10 billion base pairs is indicated. Vertical grey line indicates break in x-axis scale.
B) Heatmaps depict genomic regions (rows, n= 3,725,365 LTRs, SINEs, and LINEs) containing different repeat element families (as defined by RepeatMasker). Individual repeat elements are divided into 50 equally sized windows (5’ and 3’ position indicated). Upstream and downstream regions (±200bp) are divided into 25 equally sized windows. Panels from left to right show DNA methylation calls from 450k methylation array, RRBS, ERRBS, XRBS, and WGBS.
C) Plots compare CpG coverage within different repeat element families as a function of sequencing depth for XRBS (red), WGBS (blue), ERRBS (orange), and RRBS (green). CpG enrichment relative to WGBS is indicated. In comparison to RRBS, XRBS enriches for most repeat families, with the exception of Alu and ERV1 elements that frequently contain MspI restriction sites and are also efficiently captured (see also Extended Data Fig. 2a).