FIGURE 2:
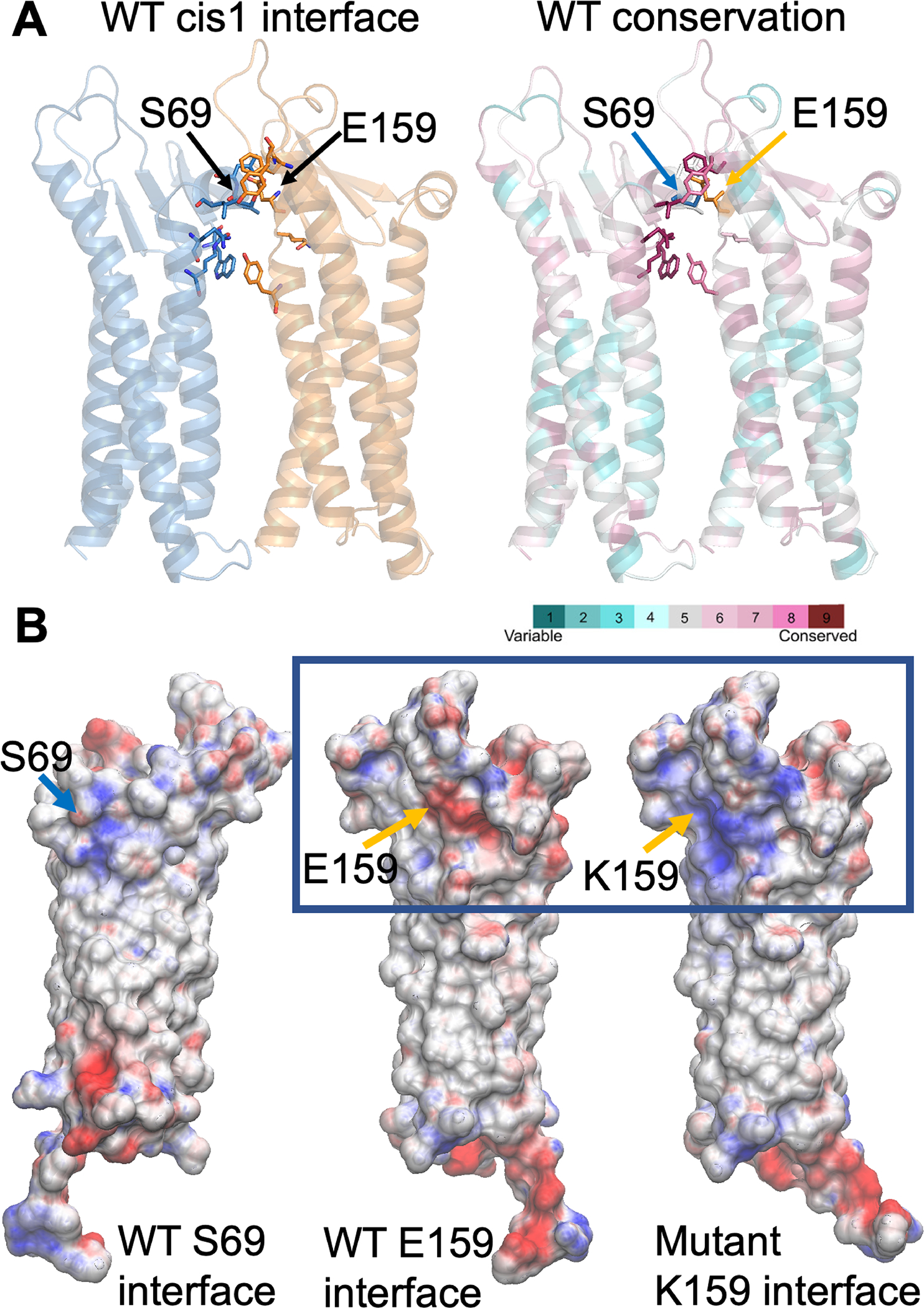
Computational modeling of human claudin 9 wild-type and mutant dimers. A, Glu-159 (E159), located in one protomer (orange in A), establishes an interaction with Ser-69 of the adjacent protomer (blue) at the dimer cis-1 interface. These residues are part of an interaction network, comprised of highly conserved residues. Both protomers in the dimer (A) are represented as cartoon (colored blue and yellow on the left and by magenta and turquoise on the right). Residues located at the interface are shown as sticks. B, The electrostatic potential at the interface between protomers (Ser-69 and Glu-159 sides or faces) for the wild-type (WT) and the Glu159Lys mutant is mapped onto the surface representation of a single protomer (B), where the residues at positions 69 and 159 are indicated as blue and orange arrows respectively. The presence of lysine (K) at position 159 shifts the electrostatic potential from negative (red) to highly positive (blue).
