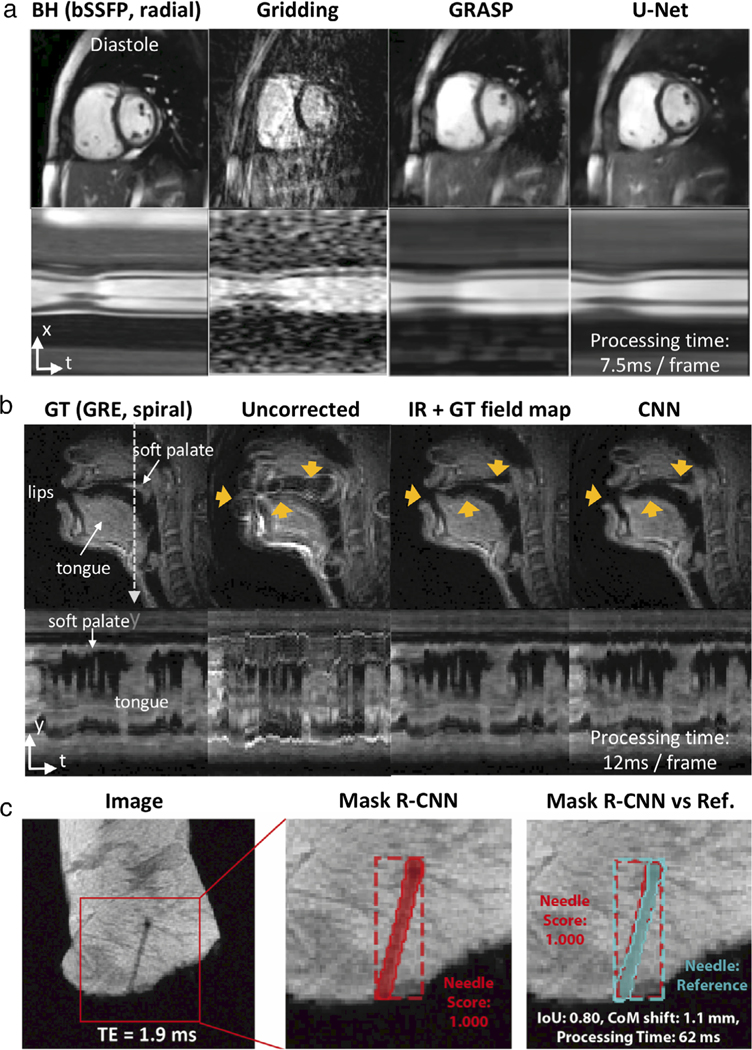
FIGURE 8:
Illustration of three ML/AI-based low-latency applications. (a) Image reconstruction of cardiovascular imaging; (left-to-right) the BH-bSSFP sequence and the RT radial sequence reconstructed with gridding, GRASP, and the residual U-Net [Adapted from Ref. (93)] (b) Spiral off-resonance deblurring of speech imaging; (left-to-right) GT, uncorrected, IR with GT field map, and the CNN [Adapted from Ref. (78)]. (C) Needle detection and segmentation for ex vivo tissue RT-MRI; (left-to-right) Original image, needle detection and segmentation result using Mask R-CNN, result comparison against a reference [Adapted from Ref. (197)]. Note that “processing time” shown here is the time to run the neural networks and does not include the time to do preprocessing of the data. BH: breath-hold, GRASP: Golden-angle radial sparse parallel imaging, PT: processing time, GT: ground truth, IR: iterative reconstruction.