FIG. 3.
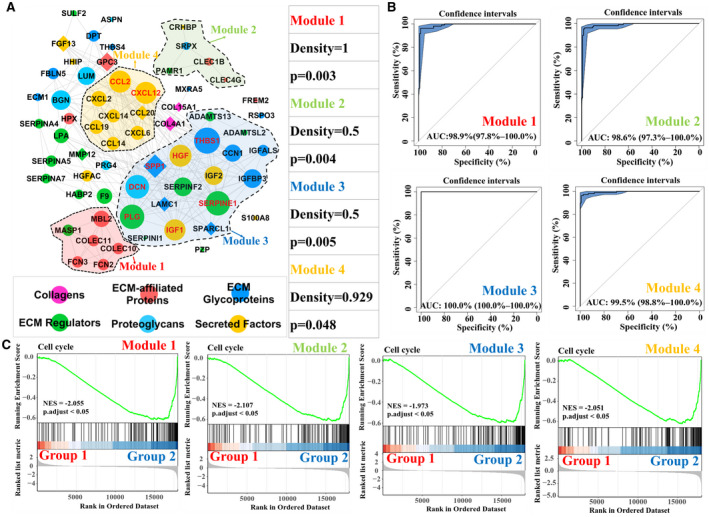
Matrisome gene modules and functional interpretation. (A) Abnormal matrisome genes’ regulatory network in HBV‐related HCC and functional modules. Significant matrisome gene modules are highlighted using different colors (P < 0.05). The node represents HHMGs, whose matrisome category is color‐coded. The edge between two nodes represents an interactive relationship. Down‐regulated HHMGs are marked using circles, and up‐regulated HHMGs are marked using diamonds. The size of the node represents the degree (i.e., the number of neighbors) of the indicated HHMG. The gene symbol of the nodes with a degree >15 is highlighted in red. (B) ROC curve analyses of four modules in the diagnosis of HBV‐related HCC from the merged samples in the GSE55092 and GSE121248 data sets. (C) GSEA analysis of the four matrisome modules. Merged samples in the GSE55092 and GSE121248 data sets were classified into two different subgroups, group 1 and group 2, based on the modular matrisome genes using HCL analysis. Adjusted P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Abbreviations: ADAMTS13, ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13; ADAMTSL2, ADAMTS‐like 2; ASPN, asporin; BGN, biglycan; CCL14, chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 14; CCL19, chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 19; CCL2, chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 2; CCL20, chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 20; CCN1, cellular communication network factor 1; CLEC1B, C‐type lectin domain family 1, member B; CLEC4G, C‐type lectin domain family 4, member G; COL15A1, collagen, type XV, alpha 1; COL4A1, collagen, type IV, alpha 1; COLEC10, collectin sub‐family member 10; COLEC11, collectin sub‐family member 11; CRHBP, corticotropin releasing hormone binding protein; CXCL12, chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 12; CXCL14, chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 14; CXCL2, chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 2; CXCL6, chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 6; DCN, decorin; DPT, dermatopontin; ECM1, extracellular matrix protein 1; F9, coagulation factor IX; FBLN5, fibulin 5; FCN2, ficolin (collagen/fibrinogen domain containing lectin) 2; FCN3, ficolin (collagen/fibrinogen domain containing) 3; FGF13, fibroblast growth factor 13; FREM2, FRAS1 related extracellular matrix protein 2; GPC3, glypican 3; HABP2, hyaluronan binding protein 2; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; HGFAC, HGF activator; HHIP, hedgehog interacting protein; IGF1, insulin‐like growth factor 1; IGF2, insulin‐like growth factor 2; IGFBP3, insulin‐like growth factor binding protein 3; LAMC1, laminin, gamma 1; LPA, lipoprotein, Lp(a); LUM, lumican; MASP1, mannan‐binding lectin serine peptidase 1 (C4/C2 activating component of Ra‐reactive factor); MMP12, matrix metallopeptidase 12; MXRA5, matrix‐remodelling associated 5; NES, normalized enrichment score; PAMR1, peptidase domain containing associated with muscle regeneration 1; PRG4, P53‐responsive gene 4; PZP, pregnancy‐zone protein; RSPO3, R‐spondin 3 homolog; S100A8, S100 calcium binding protein A8; SERPINA4, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha‐1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 4; SERPINA5, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha‐1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 5; SERPINA7, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha‐1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 7; SERPINE1, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 1; SERPINF2, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F (alpha‐2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium derived factor), member 2; SERPINI1, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade I (neuroserpin), member 1; SPARCL1, SPARC‐like 1; SPP1, secreted phosphoprotein 1; SRPX, sushi‐repeat‐containing protein, X‐linked; SULF2, sulfatase 2; THBS1, thrombospondin 1; THBS4, thrombospondin 4.
