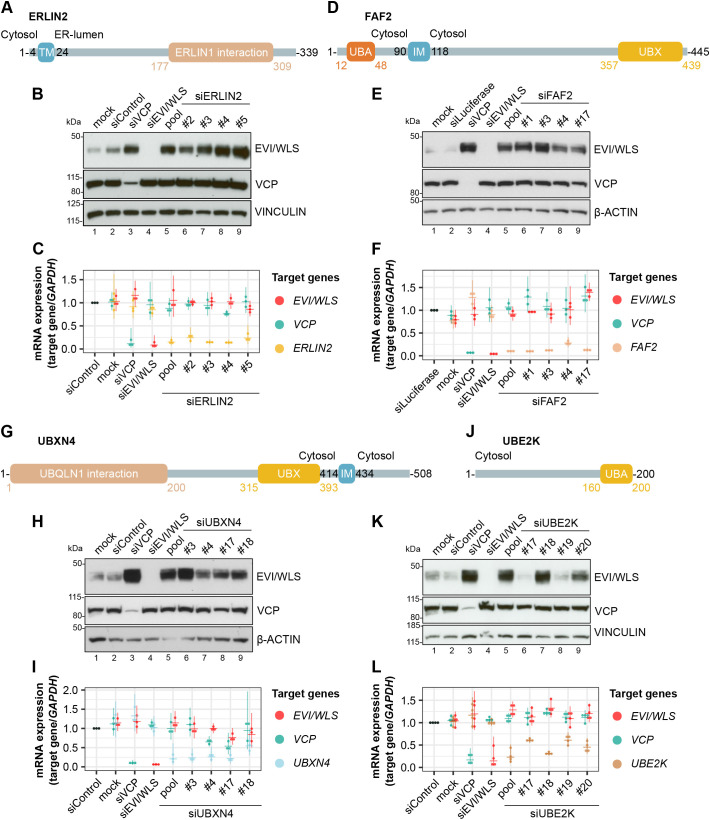
Fig. 2.
ERLIN2, FAF2, UBXN4 and UBE2K regulate endogenous EVI/WLS at the protein level. (A,D,G,J) Schematic representations of the proteins ERLIN2 (A), FAF2 (D), UBXN4 (G) and UBE2K (J) according to UniProt identifiers O94905, Q96CS3, Q92575 and P61086, respectively. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. IM, intramembrane domain; TM, transmembrane domain; UBA, ubiquitin-associated domain important for binding to ubiquitin; UBX, ubiquitin regulatory X domain important for binding to VCP. (B,C,E,F,H,I,K,L) Knockdown of ERLIN2 (B,C), FAF2 (E,F), UBXN4 (H,I) or UBE2K (K,L) increased EVI/WLS protein levels (B,E,H,K) but had no effect on EVI/WLS mRNA expression (C,F,I,L). HEK293T cells were harvested 72 h after transfection of the indicated siRNAs. siRNAs targeting ERLIN2, FAF2 or UBXN4 were used as either single siRNAs (numbered) or an equimolecular mix of all four respective siRNAs (pool). siRNA numbers are according to the manufacturer product code. Mock-transfected cells were included as a control. Vinculin (B,K) or β-actin (E,H) served as loading controls. Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. In C,F,I,L, target gene expression was normalised to siControl treatment, and GAPDH served as reference gene. Individual data points of three or four independent experiments with mean and 95% confidence intervals are shown.