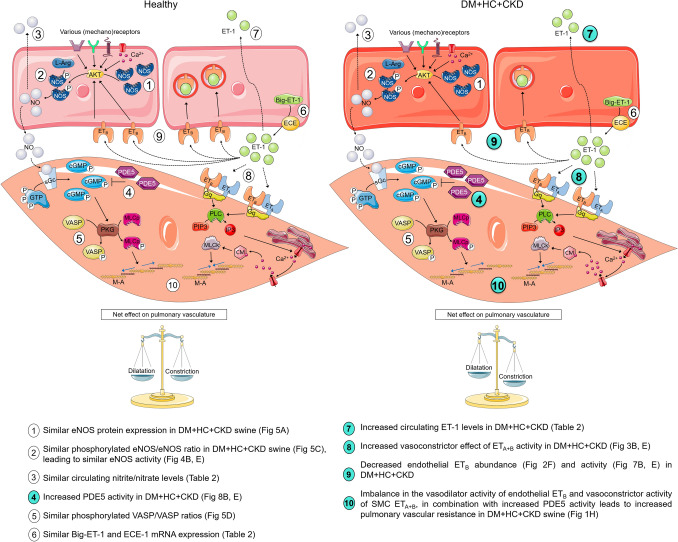
Fig. 11.
Proposed mechanisms of pulmonary vascular dysfunction in DM + HC + CKD. Upper cells represent endothelial cells, lower cells the smooth muscle cells. Significant differences in DM + HC + CKD compared to Healthy are shown as highlighted numbers in the figure. AKT protein kinase B, Big-ET-1 big endothelin 1, Ca2+ calcium, cGMP cyclic guanosine monophosphate, CM calmodulin, ECE endothelin converting enzyme, ET-1 endothelin 1, ETA endothelin receptor A, ETB endothelin receptor B, GTP guanosine triphosphate, Gq G alpha subunit, IP3 inositol triphosphate, L-Arg l-arginine, M-A myosin–actin, MLCk myosin light chain kinase, MLCp myosin light chain phosphatase, NO nitric oxide, NOS nitric oxide synthase, PDE5 phosphodiesterase 5, PIP3 phosphatidylinositol triphosphate, PKG protein kinase G, PLC phospholipase C, sGc soluble guanylate cyclase, SMC smooth muscle cell, VASP vasodilatation stimulating proteins. This figure is produced by adapting images from Servier Medical Art by Servier (https://smart.servier.com/), licensed under a Creative Commons attribution 3.0 Unported Licence