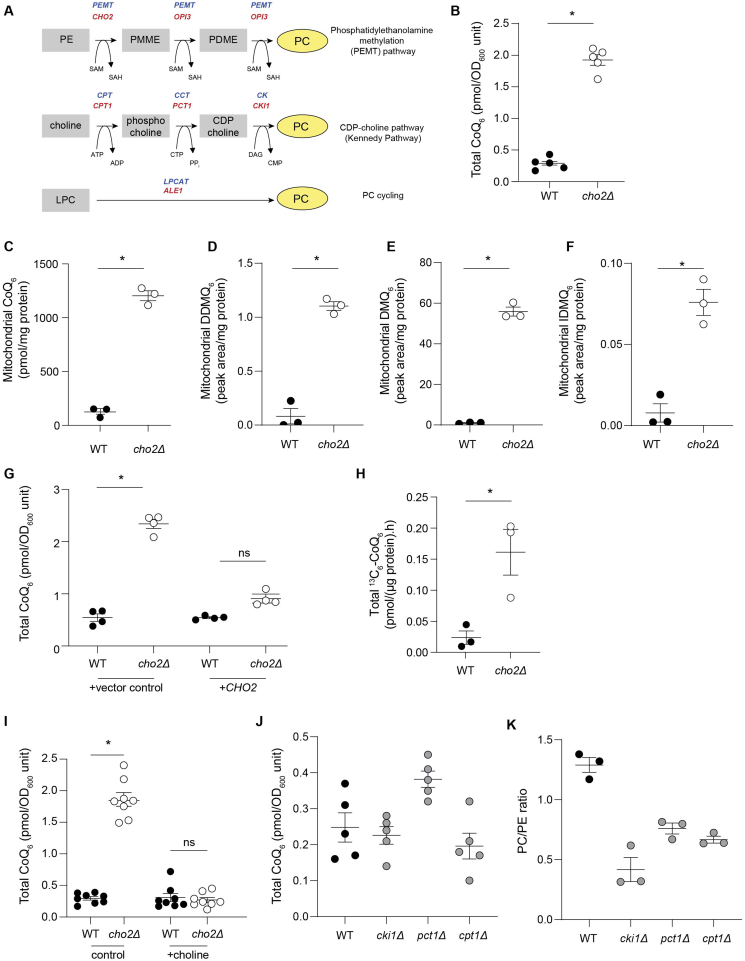
Fig. 1.
PEMT deficiency is a novel regulator of mitochondrial CoQ6content in S. cerevisiae. (A) Scheme of the three pathways that mediate phosphatidylcholine (PC) synthesis in yeast and mammals; red indicates genes in yeast, while blue indicates mammalian genes. (B) Total CoQ6 concentrations in cho2Δ mutants compared with WT (n = 5). (C) Mitochondrial CoQ6 concentrations in cho2Δ mutants compared with WT cells (n = 3). (D) Mitochondrial demethoxy-demethyl-Q6 (DDMQ6) concentrations in cho2Δ mutants compared with WT cells (n = 3). (E) Mitochondrial demethoxy-Q6 (DMQ6) concentrations in cho2Δ mutants compared with WT cells (n = 3). (F) Mitochondrial imino-demethoxy-Q6 (IDMQ6) concentrations in cho2Δ mutants compared with WT cells (n = 3). (G) Total CoQ6 concentrations in WT and cho2Δ mutants harboring either control vector or a single copy of CHO2 (n = 4). (H) CoQ6 biosynthetic rate in cho2Δ mutants and WT cells measured using the rate of 13C6-CoQ6 formed from supplemented 13C6-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4HB) (n = 3). (I) Total CoQ6 concentrations in WT and cho2Δ mutants with or without 1 mM choline supplementation (n = 8). (J) Total CoQ6 concentrations in WT and mutants of the Kennedy Pathway (n = 5). (K) PC/PE ratio in WT and mutants of the Kennedy Pathway (n = 5). Data and error bars depict mean ± s.e.m. *depicts P ≤ 0.05 and ns indicates ‘not significant’ as determined by Mann-Whitney (B–F, H) or Kruskal-Wallis (G, I–K) test. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)