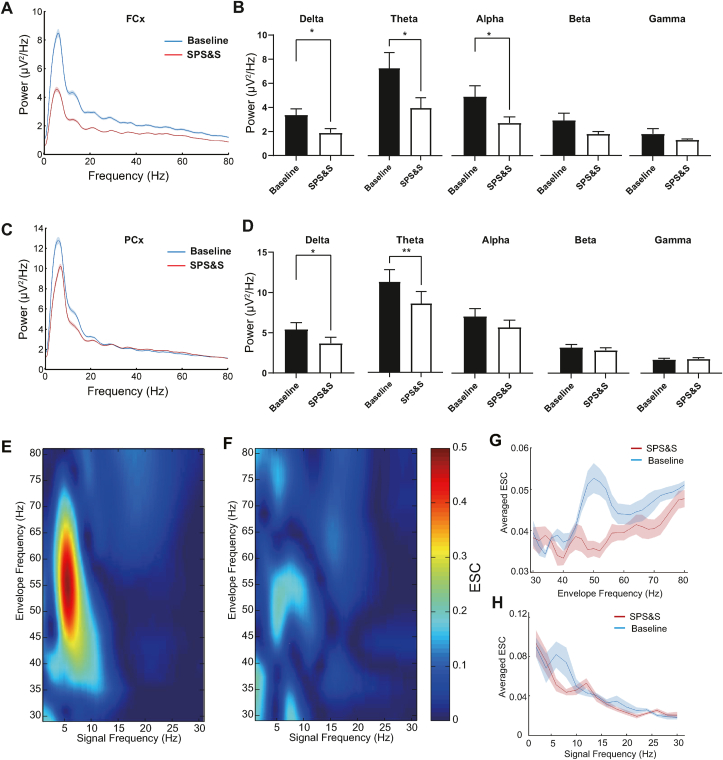
Fig. 7.
SPS&S mice show decreased EEG power spectra and FCx-PCx coupling. A Example power spectra in the FCx collected over 4 h with eyes open. b) Compared with control mice, SPS&S mice exhibited decreased delta (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 0.5090, df = 3, P = 0.0147, n = 4 per group), theta (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 4.664, df = 3, P = 0.0186, n = 4 per group), and alpha (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 4.073, df = 3, P = 0.0267, n = 4 per group) power spectra in the FCx. There was little difference in the beta (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 2.292, df = 3, P = 0.1058, n = 4 per group) and gamma (Two-tailed paired separate variance estimation t-test, t = 0.9475, df = 3, P = 0.4133, n = 4 per group). B Power spectra of SPS&S mice and control mice. C Example power spectra in the PCx collected over 4 h with eyes open. Both SPS&S mice and control mice showed peak power at theta (peak at 6 Hz), while SPS&S mice exhibited widely decreased power spectra compared with control mice. D Compared with control mice, SPS&S mice exhibited decreased delta (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 5.174, df = 3, P = 0.0140, n = 4 per group) and theta (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 10.77, df = 3, P = 0.0017, n = 4 per group) power spectra in the PCx. SPS&S mice and control mice exhibited similar alpha (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 2.627, df = 3, P = 0.0785, n = 4 per group), beta (Two-tailed paired t-test, t = 1.892, df = 3, P = 0.1548, n = 4 per group), and gamma (Two-tailed paired separate variance estimation t-test, t = 0.4021, df = 3, P = 0.7146, n = 4 per group) power spectra. E Example envelope-to-signal comodulograms obtained from EEGs between envelopes of high-frequency signals (y-axis) at FCx and raw low-frequency signals at PCx (x-axis) at baseline. The pseudocolor scale represents the ESC values shown on the right; warm colors indicate stronger modulation. Note the prominent modulation of slow gamma (40–70 Hz) peaks. F Example envelope-to-signal comodulograms obtained from EEGs between envelopes of high-frequency signals (y-axis) at FCx and raw low-frequency signals at PCx (x-axis) in SPS&S mice. Note the prominent modulation of slow gamma (40–70 Hz) peaks. G Mean ESC strength (average ESC) as a function of envelope frequency. SPS&S mice exhibited significantly weaker ESC values than control mice (Repeated measurement ANOVA, Fbetween group = 6.545, df1 = 1, df2 = 4.022, Pbetween group = 0.001; Fwithin group = 6.515, df1 = 1, df2 = 6, Pwithingroup = 0.043; *P < 0.05, n = 4 per group). H Mean ESC strength (average ESC) as a function of amplitude signal frequency. SPS&S mice exhibited little difference from control mice (Repeated measurement ANOVA, Fbetween group = 16.206, df1 = 1, df2 = 14, Pbetween group < 0.0001; Fwithin group = 1.340, df1 = 1, df2 = 6, Pwithingroup = 0.277; n = 4 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. . (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)