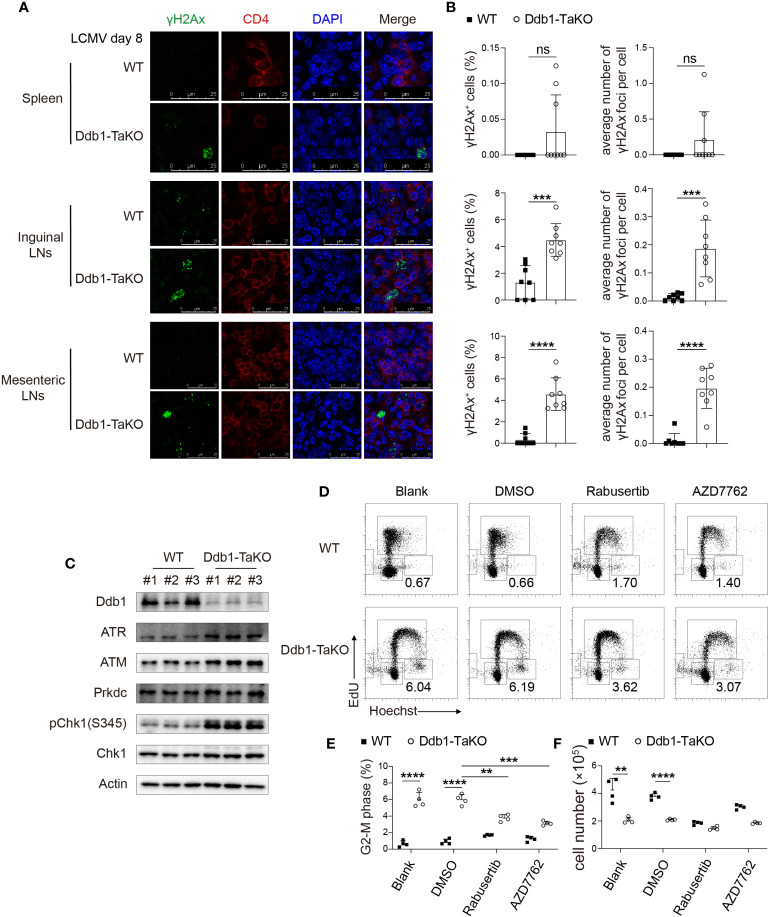
Figure 7.
Ddb1 deficiency causes accumulation of DNA damage and hyper-activation of ATM/ATR-Chk1 pathway. (A) Immunofluorescence of γH2Ax frozen sections in the spleen, inguinal LNs, and mesenteric LNs from WT and Ddb1-TaKO mice at day 8 after LCMV Armstrong infection. (B) Frequency of γH2Ax+ activated CD4+ T cells and the number of γH2Ax foci per cell were quantitated. (C) Immunoblot analysis of lysates of Ddb1-TaKO and WT activated CD4+ T cells at day 3 in Figure 5C, probed with antibodies to Chk1 signaling related proteins. (D) Cell cycle analysis of CD4+ T cells treated with Chk1 inhibitors by EdU incorporation assay at day 3 in Figure 5C. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas indicate percentage of CD4+ T cells at G2-M phase. (E) Frequency of CD4+ T cells at G2-M phase in (D). (F) Total number of activated CD4+ T cells in (D) Each symbol represents an individual mouse or individual well of cells, small horizontal lines indicate the mean ( ± s.d.). ns, not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (Student’s unpaired t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (error bars, s.d.).