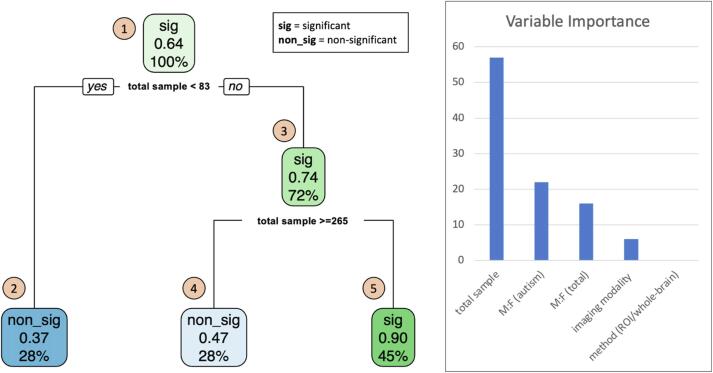
Fig. 5.
Decision tree – exploring the most important factor associated with the significance of reported sex/gender-by-diagnosis interaction effects and sex/gender-stratified autism-control differences from studies reviewed (N = 69). Findings from studies are coded by a binary variable, ‘significance’, where positive/significant findings are coded ‘1’ and negative non-significant findings are coded ‘0’ and expressed as a function of study features included total sample size, male-to-female participant ratio (total sample), male-to-female participant ratio (autism group), method (i.e., region-of-interest, whole-brain), and imaging modality. At the top of the decision tree, (1) the proportion of studies that reported a significant finding is 64%. (2) The first node asks whether the total sample size of the study is less than 83. 28% of the studies include a total sample size less than 83 where the probability of reporting a significant finding is 37%. (3) 72% of the studies include a total sample size greater than or equal to 83 where the probability of reporting a significant finding is 74%; however, (4) this probability decreases to 47% if the total sample size is greater than or equal to 265 and (5) increases to 90% if the total sample size is less than 265.