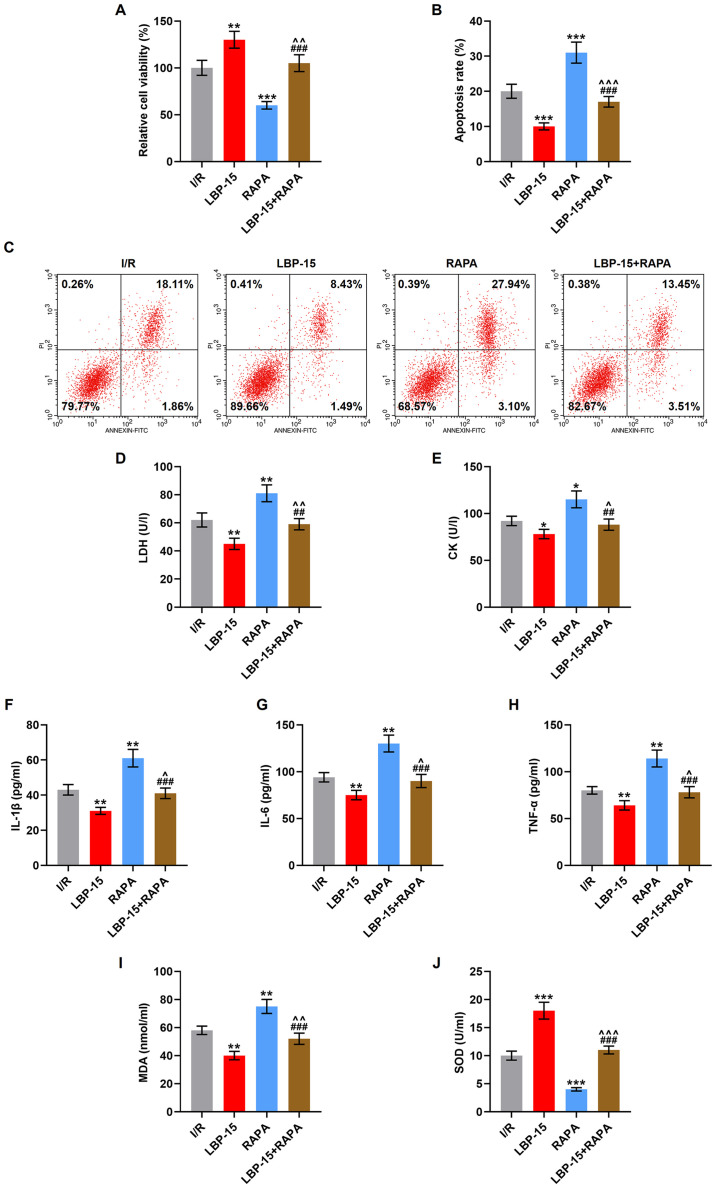
Figure 5.
RAPA partially reverses the LBP-induced increase of viability and inhibition of apoptosis, cardiomyocyte damage, inflammation and oxidative stress in I/R-induced H9C2 cells. (A) The viability of I/R-induced H9C2 cells with the treatment of LBP (15 µg/ml) and RAPA in combination or alone was determined using an MTT assay. (B) The apoptosis of I/R-induced H9C2 cells with the treatment of LBP (15 µg/ml) and RAPA in combination or alone was detected via (C) flow cytometry. The levels of (D) LDH, (E) CK, (F) IL-1β, (G) IL-6, (H) TNF-α, (I) MDA and (J) SOD in I/R-induced H9C2 cells with the treatment of LBP (15 µg/ml) and RAPA in combination or alone were determined via ELISAs. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. I/R; ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01, ^^^P<0.001 vs. LBP-15; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs. RAPA. I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; LBP, Lycium barbarum polysaccharide; RAPA, rapamycin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CK, creatine kinase; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxidase dismutase.