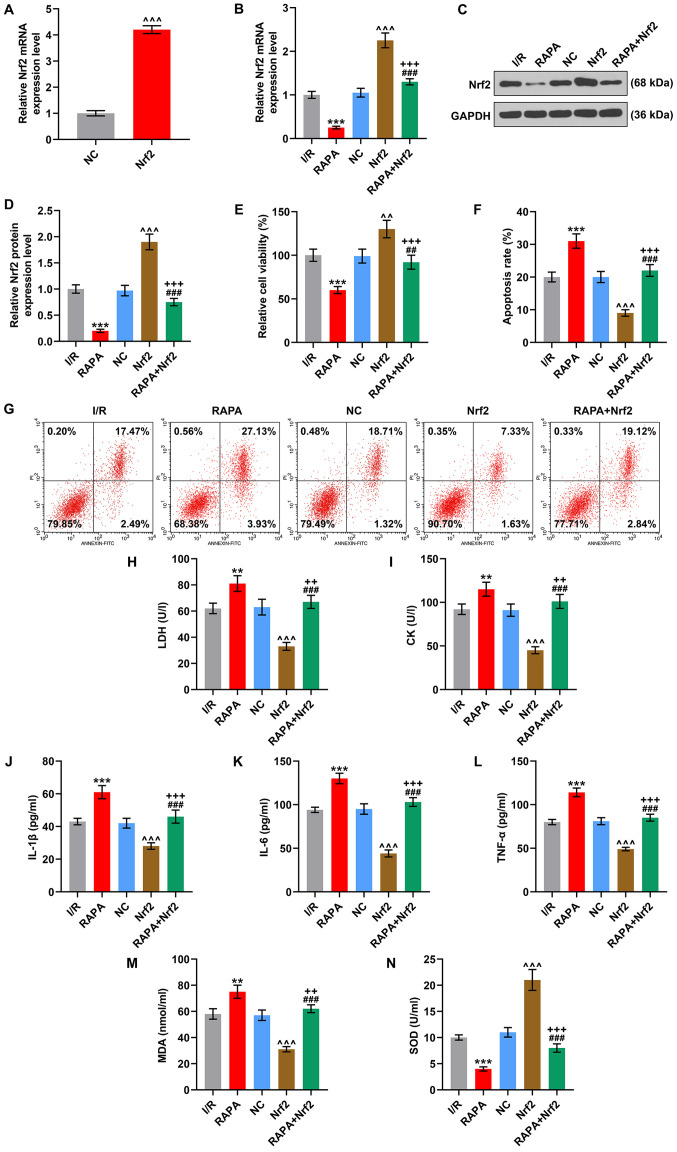
Figure 7.
Nrf2 partially reverses RAPA-induced decrease of viability, promotion of apoptosis, cardiomyocyte damage, inflammation and oxidative stress in I/R-induced H9C2 cells. (A) The transfection efficiency of Nrf2 overexpression plasmid in normal H9C2 cells. The (B) mRNA and (C and D) protein expression levels of Nrf2 in I/R-induced H9C2 cells with transfection of Nrf2 overexpression plasmid, RAPA treatment or the combined management were quantified by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and western blotting. GAPDH was used as internal reference. (E) The viability of I/R-induced H9C2 cells undergoing transfection of Nrf2 overexpression plasmid, RAPA treatment or the combined management was determined using an MTT assay. (F) The apoptosis of I/R-induced H9C2 cells after the transfection of Nrf2 overexpression plasmid, RAPA treatment or the combined management was detected via (G) flow cytometry. The levels of (H) LDH, (I) CK, (J) IL-1β, (K) IL-6, (L) TNF-α, (M) MDA and (N) SOD in I/R-induced H9C2 cells undergoing transfection of Nrf2 overexpression plasmid, RAPA treatment or the combined management were calculated using ELISAs. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. I/R; ^^P<0.01, ^^^P<0.001 vs. NC; ++P<0.01, +++P<0.001 vs. RAPA; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs. Nrf2. NC, empty pcDNA3.1 vector as negative control; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; LBP, Lycium barbarum polysaccharide; RAPA, rapamycin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CK, creatine kinase; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxidase dismutase.